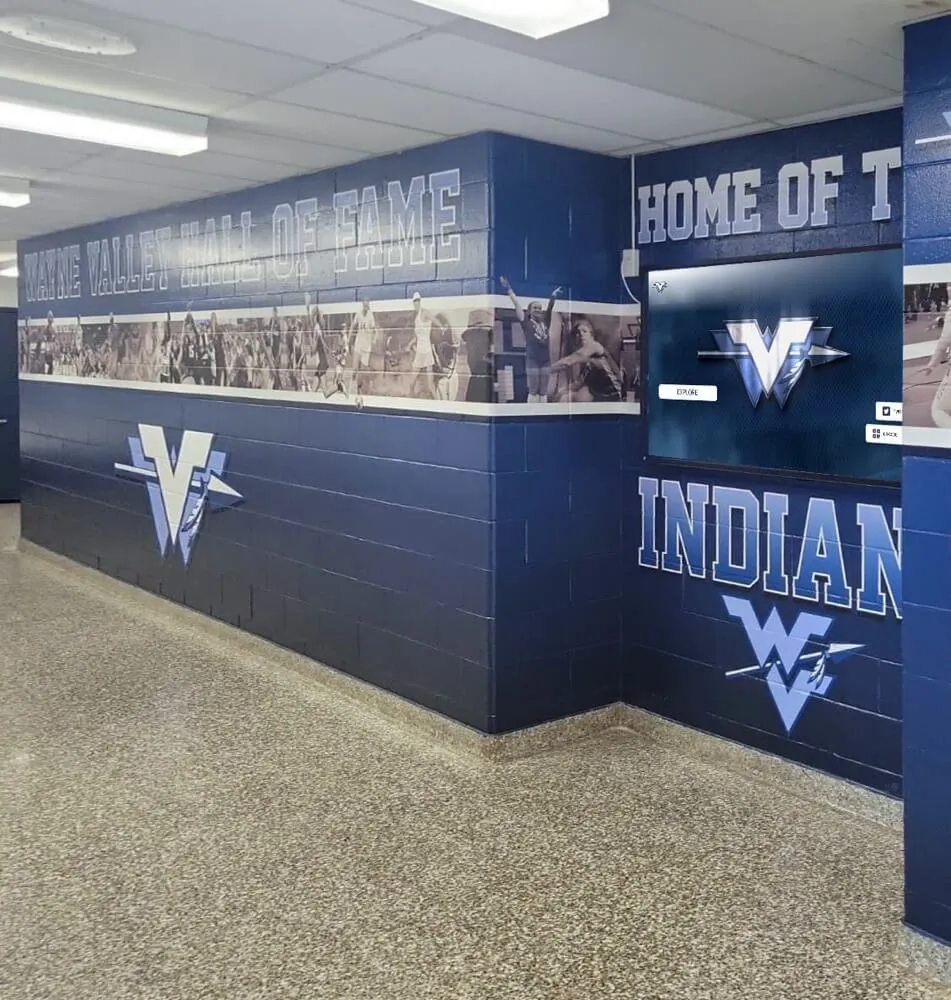
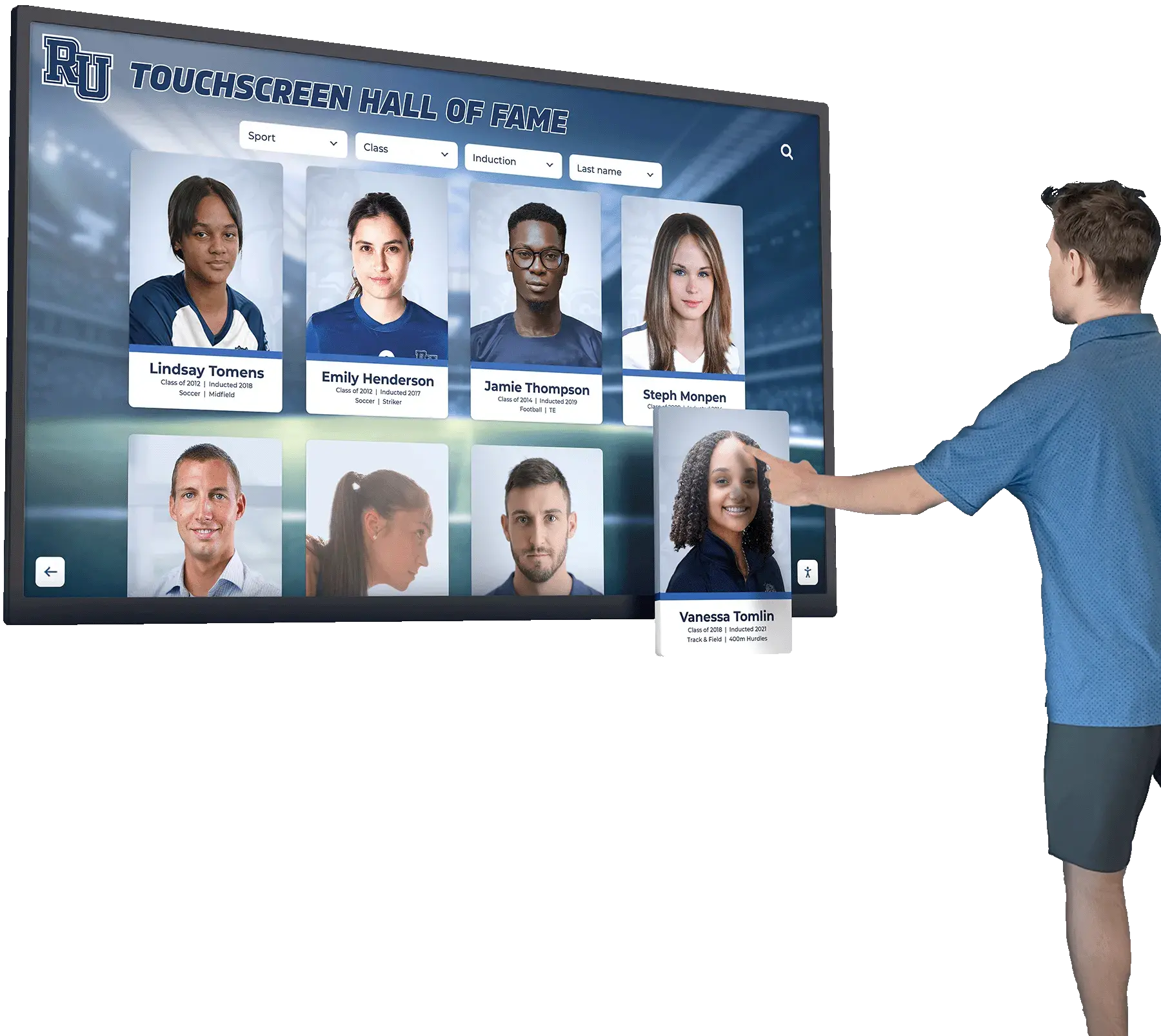
Touchscreen kiosks at events, trade shows, and product demonstrations transform passive exhibit spaces into interactive experiences that capture attention, communicate complex information clearly, and create memorable connections between audiences and products. Equipment manufacturers face unique challenges showcasing technical features to diverse audiences ranging from industry experts to potential end-users who need accessible explanations without overwhelming technical jargon.
Traditional static displays with printed specifications and manual demonstrations limit engagement while failing to adapt content to visitor knowledge levels. Modern touchscreen technology enables dynamic, self-guided exploration where visitors control the pace and depth of information they receive, accessing technical specifications, visual demonstrations, application examples, and comparison tools through intuitive interfaces designed for diverse audiences and varying event environments.
This comprehensive guide explores how to develop, implement, and optimize touchscreen kiosk technology for events and functions, providing equipment manufacturers with frameworks for creating interactive product explanation tools that work effectively across websites, mobile devices, and physical touchscreen displays during exhibitions, trade shows, product launches, and customer events.
Equipment manufacturers need flexible technology solutions that work consistently across multiple platforms while highlighting product differentiation through clear, accessible feature explanations. Whether presenting at industry conferences, customer appreciation events, product launch functions, or ongoing showroom installations, interactive touchscreen technology creates self-service information access that reduces staff burden while improving visitor understanding and engagement.

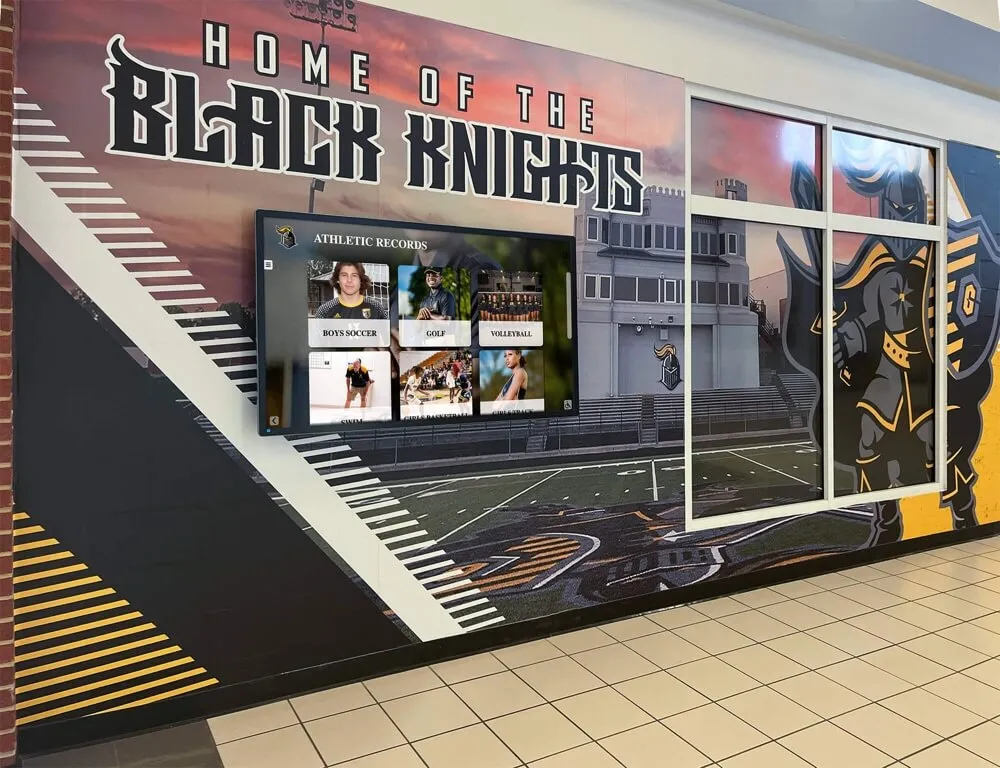
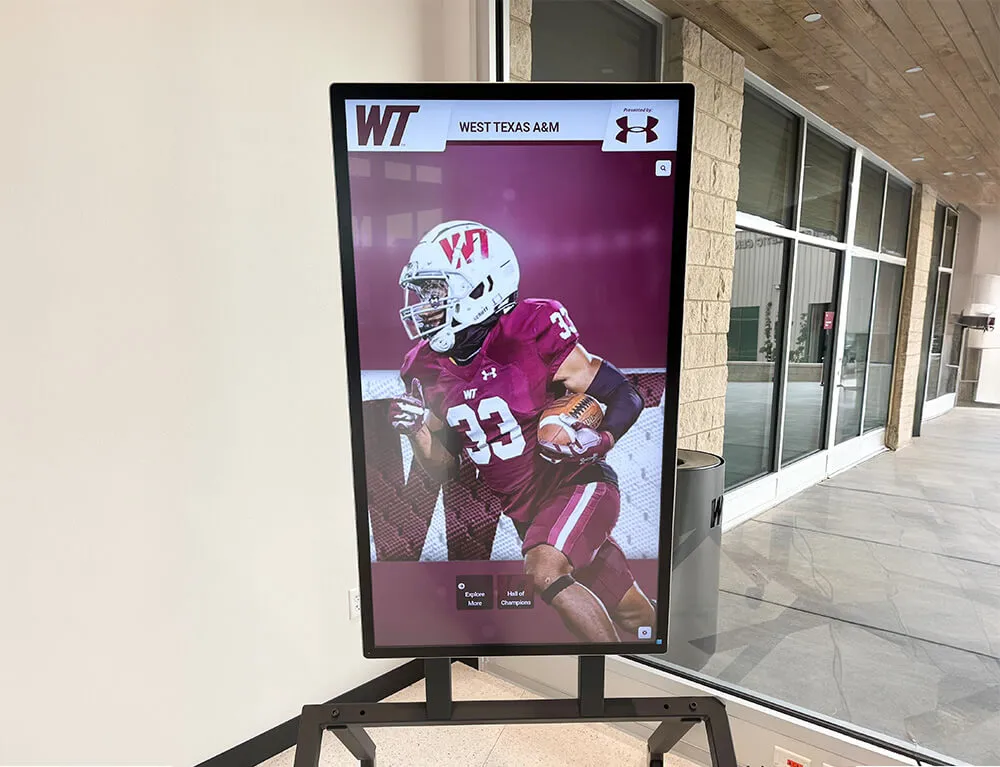
Professional event environments benefit from interactive touchscreen technology that enables self-guided product exploration and demonstration
Understanding Touchscreen Technology for Events
Before selecting specific hardware or software solutions, understanding the distinct requirements of event-based touchscreen deployments helps manufacturers avoid common pitfalls while building systems that perform reliably in challenging event environments.
Event Environment Considerations
Event and function environments present unique technical challenges compared to permanent installations in controlled settings.
Physical Environment Factors significantly impact hardware selection and system design. Trade show floors experience high traffic, frequent bumps and touches, variable lighting from bright booth lights to dimmed exhibition halls, temperature fluctuations from HVAC systems and crowd density, and ambient noise requiring clear visual communication without audio dependence.
Network and Connectivity Challenges require careful planning since event venues rarely provide reliable infrastructure. Systems must function effectively with limited or unreliable WiFi, support offline operation when network access fails, enable quick setup without complex network configuration, allow content updates through mobile hotspots or cellular connections, and maintain performance despite bandwidth constraints affecting multiple exhibitors.
Setup and Breakdown Requirements differentiate event technology from permanent installations. Equipment must survive frequent transportation, support rapid deployment by non-technical staff, enable simple calibration and configuration without specialized tools, withstand repeated assembly and disassembly cycles, and pack efficiently for shipping between events.
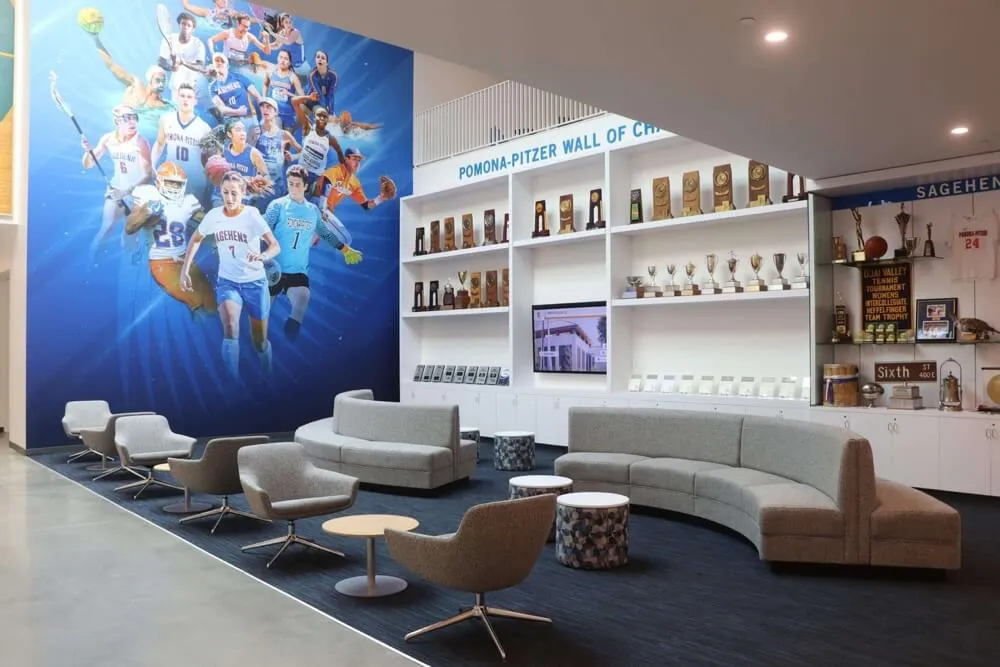
Interactive kiosk solutions designed for high-traffic public environments often translate well to event applications when properly adapted for mobile deployment scenarios.
Platform Requirements for Multi-Device Deployment
Effective product explanation tools must function consistently across websites, tablets, mobile phones, and large-format touchscreen displays without requiring separate development for each platform.
Responsive Design Principles ensure content adapts appropriately to different screen sizes and interaction methods. Interfaces must scale from smartphone screens to 55-inch touchscreen displays, support both touch and traditional mouse/keyboard input, maintain readability across resolution ranges, adapt navigation patterns to available screen space, and optimize performance for varying device capabilities.
Content Management Flexibility enables updating information across all platforms simultaneously. Centralized content repositories eliminate version inconsistencies, cloud-based systems support remote updates during events, modular content architecture allows platform-specific optimization, automated publishing workflows maintain consistency, and version control prevents outdated information from appearing on any platform.
Progressive Enhancement Approaches ensure basic functionality works universally while providing enhanced experiences where capabilities exist. Core product information remains accessible without advanced features, interactive visualizations degrade gracefully to static images when needed, video content includes alternative text descriptions, touch-optimized controls work with mouse input, and offline caching maintains functionality during connectivity loss.

Permanent installations demonstrate touchscreen interface patterns that translate effectively to temporary event deployments
Content Strategy for Product Feature Highlights
Compelling content strategy determines whether touchscreen investments deliver value or become expensive digital brochures that visitors ignore after brief initial interaction.
Audience-Appropriate Information Architecture
Different visitor segments seek different information depth requiring flexible navigation supporting varied exploration patterns.
Technical Audience Pathways serve engineers, procurement specialists, and industry experts seeking detailed specifications. These users need direct access to engineering drawings and CAD files, comprehensive specification sheets with all technical parameters, comparison matrices against competitive products, compatibility documentation for integration scenarios, certification and compliance documentation, and performance data under various operating conditions.
Decision-Maker Pathways address executives and managers focused on business impact rather than technical minutiae. This audience requires ROI calculators and cost-of-ownership analysis, case study summaries demonstrating application success, competitive differentiation explanations without excessive jargon, implementation timeline estimates, support and warranty information, and clear value proposition statements linking features to business outcomes.
End-User Pathways help operators and maintainers understand practical product use. These visitors benefit from operational walkthroughs showing common procedures, maintenance requirement summaries with schedules, troubleshooting guides for typical issues, safety information and best practices, training resource availability, and real-world application videos showing products in use.
Discovery Pathways support visitors without pre-existing knowledge who need basic orientation. This group responds to visual product overviews with minimal text, application category browsing by industry or use case, guided tours highlighting key differentiators, comparison tools helping identify appropriate models, and clear next-step calls to action connecting to sales resources.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions demonstrate effective multi-audience content architecture through digital signage platforms designed to serve diverse user needs through intuitive navigation and layered information access.
Dynamic Content Modules
Modular content architecture enables mixing and matching information elements appropriate for specific products, audiences, and event contexts.
Product Overview Modules provide foundational information establishing context before detailed exploration. Elements include high-quality product photography from multiple angles, 3D model viewers enabling rotation and zoom, specification summary cards highlighting key features, application category identification, size and configuration options, and pricing tier indicators or contact prompts.
Feature Explanation Modules break complex capabilities into digestible components. Effective modules present one feature per screen or section, combine visual demonstrations with concise text explanations, show benefit statements answering “why this matters,” include comparison points against standard alternatives, link technical specifications to practical outcomes, and provide deeper technical resources through expanding sections or linked documents.
Application Showcase Modules demonstrate products solving real problems in context. Strong application content includes industry-specific use cases, before-and-after scenarios showing improvement, customer environment photos (when permitted), workflow diagrams showing integration, performance metrics from real deployments, and video demonstrations in actual operating environments.
Interactive Tool Modules transform passive consumption into active engagement. Valuable tools include product configurators building custom solutions, ROI calculators estimating value delivery, comparison selectors contrasting models or competitors, specification filters identifying appropriate products, sizing calculators determining requirements, and diagnostic tools helping identify needed solutions.
Support and Resource Modules connect visitors to deeper information and human assistance. Essential resources include downloadable literature (PDFs, CAD files), contact forms with context about current product interest, live chat or video call options during staffed hours, training video libraries, FAQ sections addressing common questions, and warranty and support policy information.

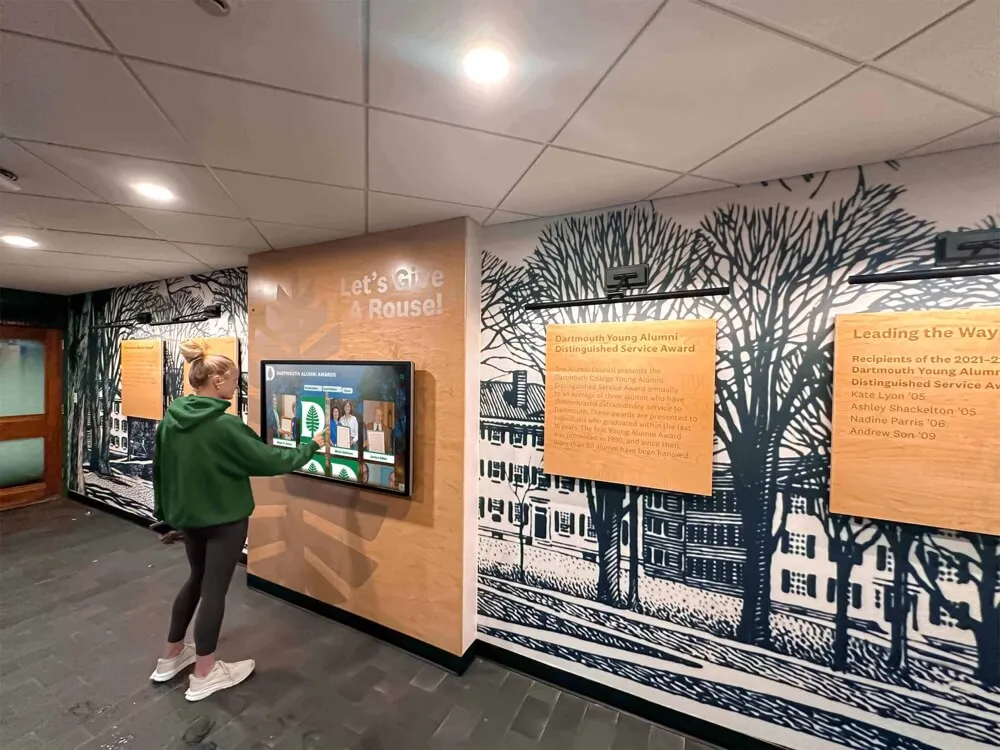
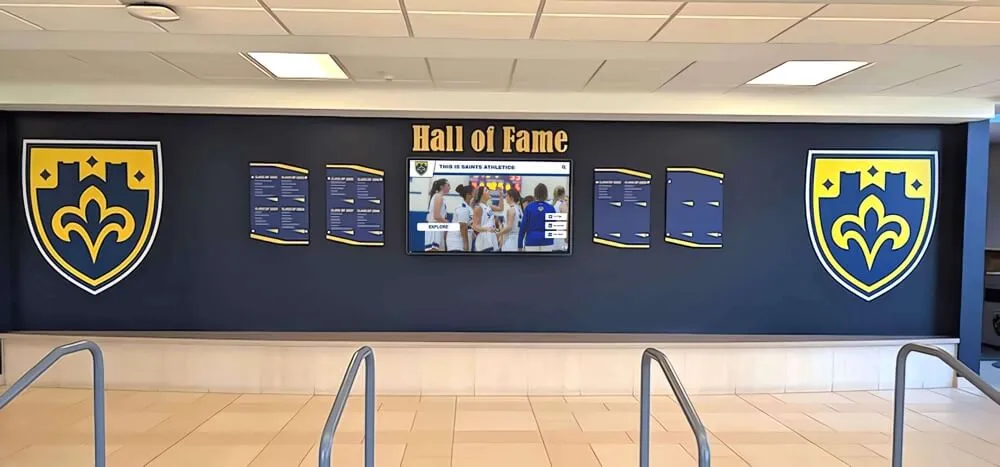
Intuitive touch interfaces enable visitors to explore detailed information at their own pace without staff assistance
Technical Implementation Approaches
Selecting appropriate technology platforms and implementation approaches determines long-term flexibility, maintenance requirements, and total cost of ownership beyond initial development investment.
Web-Based vs. Native Applications
Fundamental platform decisions affect compatibility, maintenance, and capability trade-offs requiring careful evaluation against specific requirements.
Web-Based Touchscreen Applications use standard browser technology running on any device with current web browsers. This approach provides universal compatibility across platforms and devices, eliminates app store approval processes and restrictions, enables instant updates deployed to all installations simultaneously, supports access through both dedicated kiosks and visitor devices, reduces development cost through single codebase, and simplifies maintenance through centralized hosting.
Web platform limitations include potential performance constraints for complex visualizations, offline functionality requiring progressive web app architecture, browser compatibility testing across multiple versions, and internet connectivity dependency unless offline-first architecture implemented.
Native Applications built for specific operating systems provide maximum performance and integration but increase complexity. Benefits include superior performance for graphics-intensive content, complete offline functionality without connectivity, access to device-specific hardware features, better control over user experience and security, and potential for app store distribution reaching broader audiences.
Native application drawbacks include separate development for iOS, Android, and Windows increasing cost, app store approval requirements and restrictions, update deployment requiring user action rather than automatic, and maintenance complexity managing multiple codebases across platforms.
Touchscreen software platforms designed for institutional environments often balance these considerations through hybrid approaches combining web technology with native containers providing device access.
Hybrid and Progressive Web App Approaches increasingly provide middle-ground solutions combining web development efficiency with native-like functionality. Modern frameworks enable web applications that install to home screens, function completely offline after initial load, access device hardware through standard web APIs, deliver near-native performance through optimization, and deploy through both web hosting and app stores when needed.
Hardware Selection for Event Environments
Appropriate hardware choices ensure reliable operation through repeated transport, setup, and intensive use cycles that destroy consumer-grade equipment.
Commercial-Grade Touch Displays rated for continuous operation and public interaction survive event environments where consumer screens fail. Essential specifications include commercial display ratings for 24/7 operation, optical bonding reducing glare and improving image quality, anti-glare and anti-fingerprint coatings maintaining visibility, vandal-resistant construction surviving aggressive touch, wide viewing angles supporting multiple simultaneous viewers, and brightness levels exceeding 500 nits for well-lit environments.
Mounting and Enclosure Systems protect displays while providing professional appearance and cable management. Effective mounting solutions include VESA-compatible wall mounts for various sizes, freestanding kiosk enclosures for self-contained installations, portable stands with equipment storage and cable management, locking mechanisms preventing theft at events, integrated power and connectivity management, and modular designs allowing display replacement without replacing entire kiosks.
Computing and Media Players must provide adequate performance while maintaining reliability and easy replacement. Appropriate choices include commercial media players designed for digital signage, small form-factor PCs with adequate graphics performance, reliable solid-state storage without moving parts, adequate RAM for smooth application performance, appropriate network connectivity (WiFi and Ethernet), and standardized components allowing quick replacement without custom ordering.
Peripheral Considerations enhance functionality while introducing potential failure points requiring backup plans. Useful peripherals include printers providing takeaway materials or lead capture, card readers for attendee badge scanning and tracking, cameras enabling photo capture or QR code scanning, audio systems supporting video content in appropriate environments, and environmental sensors triggering content changes.
Content Management and Update Systems
Effective content management enables maintaining current information across multiple deployment locations without requiring physical access to each installation.
Cloud-Based Content Platforms provide centralized control with remote update capability. Essential features include web-based administration accessible from any device, scheduling systems controlling content timing, multi-device management tracking all installations, user permission systems controlling access, content approval workflows preventing unauthorized changes, version history enabling rollback when needed, and analytics tracking usage and engagement.
Offline Operation and Sync ensure reliability when network connectivity fails at venues. Robust systems cache all content locally on devices, detect network status and switch modes automatically, queue updates for synchronization when connected, provide manual sync triggering when needed, alert administrators to sync failures, and maintain functionality throughout connectivity gaps.
Content Creation and Publishing Workflows determine how efficiently teams can update information. Efficient workflows support drag-and-drop content editing without coding, media library management organizing assets, preview systems showing changes before publishing, template systems maintaining consistency, multi-user collaboration with role assignments, and integration with existing content management systems.
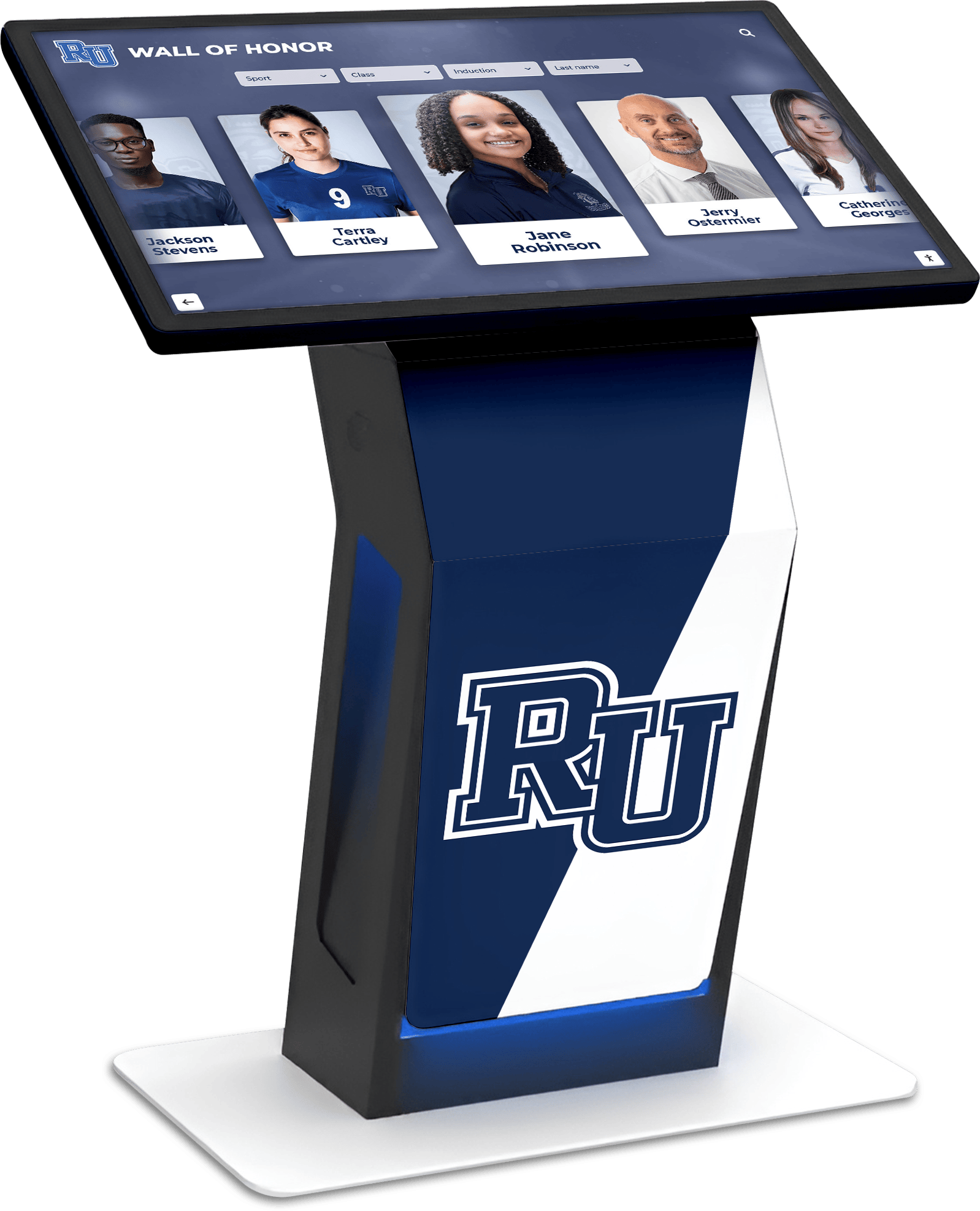

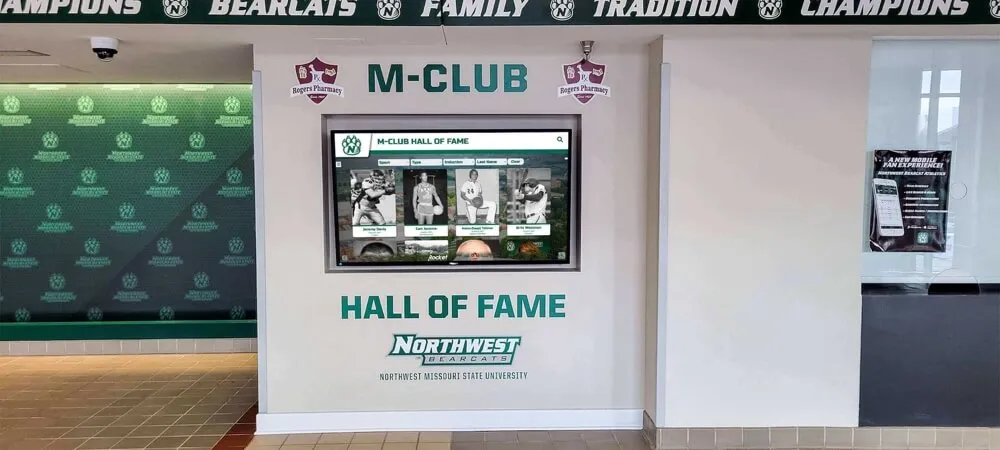
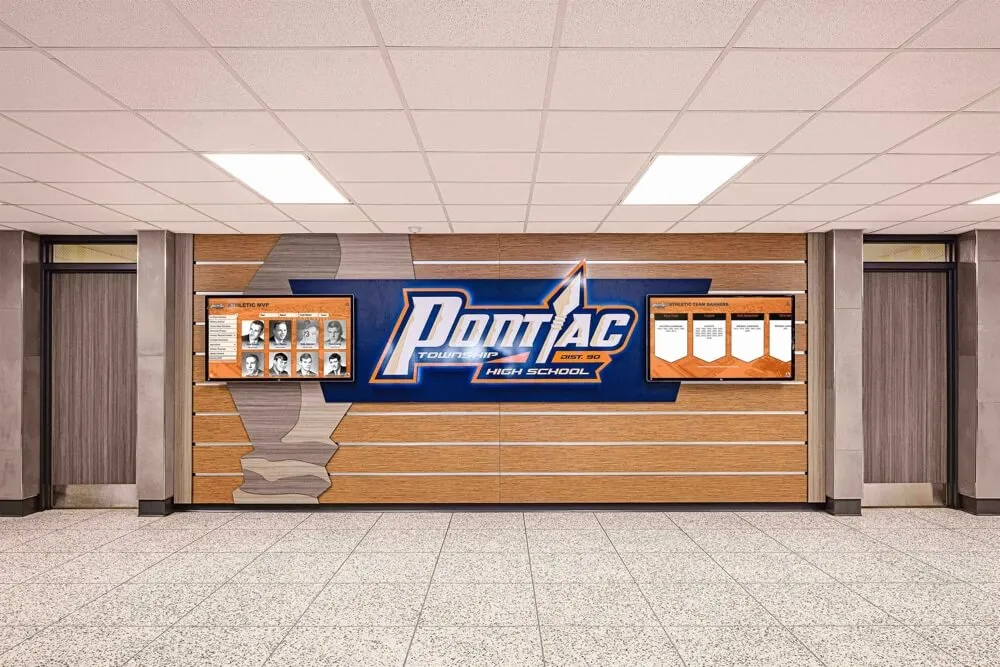
Professional kiosk installations demonstrate content management approaches supporting dynamic, regularly updated information
Design Principles for Event Touchscreens
Interface design determines whether visitors engage deeply with content or abandon after brief interaction, making design decisions as important as technical platform choices.
Touch-Optimized Interface Design
Touchscreen interactions require different interface approaches than traditional mouse-and-keyboard or mobile phone interfaces.
Touch Target Sizing and Spacing prevents accidental activation and user frustration. Minimum touch target sizes of 44-48 pixels (approximately 10-12mm physical) ensure reliable activation, adequate spacing between targets prevents accidental adjacent selection, larger targets for primary actions guide user focus, consistent target sizing throughout interface builds user confidence, and buffer zones around critical actions prevent mistakes.
Navigation Patterns for Standing Users accommodate visitors who spend seconds to minutes at displays without sitting. Effective patterns include persistent navigation visible from all screens, clear visual hierarchy guiding attention flow, home/back buttons always accessible, progress indicators showing position in multi-step processes, timeout warnings before returning to attract mode, and gesture support (swipe, pinch) for intuitive interaction.
Visual Hierarchy and Information Density balance comprehensive information with digestible presentation. Strong visual design establishes clear entry points drawing attention, uses progressive disclosure revealing detail gradually, maintains generous white space preventing overwhelming density, employs consistent typography with adequate sizing for reading distance, provides clear section separation through space and visual treatment, and limits simultaneous on-screen choices preventing decision paralysis.
Color, Contrast, and Accessibility ensure visibility across lighting conditions and user abilities. Accessible design requires high contrast ratios meeting WCAG standards, color schemes tested under various lighting conditions, information conveyed through multiple channels (not color alone), text sizing supporting readability from typical distances, and alternative interaction methods accommodating different abilities.
Content Presentation Strategies
How information appears determines whether visitors understand key messages or become confused by complexity.
Chunking and Progressive Disclosure break complex information into manageable segments. Effective approaches present overview information first with option to explore details, use expandable sections revealing additional information, implement multi-screen flows for complex processes, provide clear “learn more” paths for interested visitors, maintain context during deeper exploration, and offer easy return to overview level.
Visual Communication Over Text leverages graphics, icons, and imagery carrying meaning efficiently. Strong visual communication uses high-quality product photography showing important features, icons and graphics reinforcing text meaning, infographics explaining complex relationships or processes, videos demonstrating products in action, diagrams showing component relationships or workflows, and charts visualizing performance data or comparisons.
Animation and Motion Design attracts attention while communicating function when used appropriately. Effective motion includes attract mode animations drawing passing visitors, transitions reinforcing relationships between screens, loading indicators maintaining engagement during waits, subtle animations indicating touch response, directional motion guiding attention flow, and performance optimization preventing lag or stutter.
Multimedia Integration provides varied content types supporting different learning preferences. Valuable multimedia includes product demonstration videos with clear audio and captions, 360-degree product viewers enabling inspection, annotated technical drawings highlighting key features, customer testimonial videos (when appropriate), process animations showing operation or installation, and audio narration option for accessibility.
Event-Specific Implementation Considerations
Beyond general touchscreen design principles, event-specific factors determine success in temporary deployment scenarios.
Pre-Event Preparation and Testing
Thorough preparation prevents embarrassing failures when systems activate in front of potential customers and industry peers.
Content Verification and Updates ensure information accuracy and relevance. Pre-event checks include verifying all product information reflects current specifications, confirming pricing and availability information accuracy, testing all links and interactive features, loading event-specific content (show specials, demonstrations), updating staff contact information, and preparing offline backup content files.
Technical Testing Protocols catch issues before they disrupt events. Comprehensive testing includes full system functionality checks with all features, network connectivity testing under various conditions, offline operation verification, battery life testing for portable components, touch calibration and responsiveness verification, audio and video playback quality checks, and stress testing with extended operation and multiple interactions.
Backup and Contingency Planning prepares responses to predictable failures. Essential preparations include backup devices or components for critical failures, offline content versions for network issues, printed materials supplementing digital content, staff training on troubleshooting common problems, technical support contact information, and documented recovery procedures.
Staff Training and Familiarization ensures personnel can assist visitors and troubleshoot problems. Effective training covers system navigation and key content locations, common visitor questions and where answers appear, basic troubleshooting for typical problems, how to restart or reset systems, where to direct technical issues beyond basic troubleshooting, and demonstration of key features or interactive tools.
On-Site Setup and Configuration
Efficient setup processes minimize booth preparation time while ensuring reliable operation throughout events.
Physical Installation Best Practices provide stable, safe installations in temporary environments. Important considerations include secure mounting preventing tip-over in crowded environments, cable management preventing trip hazards, power supply reliability with appropriate backup, position optimization for visibility and traffic flow, lighting angle adjustment minimizing screen glare, and accessibility ensuring wheelchair and varied-height user access.
Network Configuration and Connectivity establish reliable communication in challenging venue environments. Setup priorities include testing venue WiFi before relying on it, mobile hotspot backup for critical connectivity, VPN configuration for secure data transmission, bandwidth management for multiple devices, network timeout handling and retry logic, and monitoring systems alerting to connectivity loss.
Content Synchronization and Verification confirm all devices display current information. Essential checks include syncing latest content to all devices before events, verifying media files loaded correctly and play properly, testing interactive features and user flows, confirming contact forms and lead capture function, validating external links and resources, and documenting any last-minute content changes needed.
During-Event Management
Active monitoring and management maintain system reliability throughout events while capturing valuable engagement data.
Performance Monitoring identifies problems before they significantly impact visitor experience. Monitoring approaches include periodic functionality spot-checks throughout days, screen health checks for damage or calibration issues, interaction observation noting user difficulties, content effectiveness assessment watching engagement, network and system connectivity verification, and visitor feedback collection about experience.
Lead Capture and Analytics transform visitor interactions into actionable business intelligence. Valuable data includes interaction tracking showing popular content and features, session duration and navigation path analysis, contact information collection through opt-in forms, badge scanning linking interactions to attendee profiles, content download tracking, and survey responses gathering qualitative feedback.
Real-Time Content Adjustment responds to observed usage patterns and changing event circumstances. Useful adjustments include highlighting products generating unusual interest, addressing questions appearing in multiple conversations, promoting time-sensitive demonstrations or presentations, adjusting information depth based on audience sophistication, and rotating content preventing repetitive experience for repeat visitors.
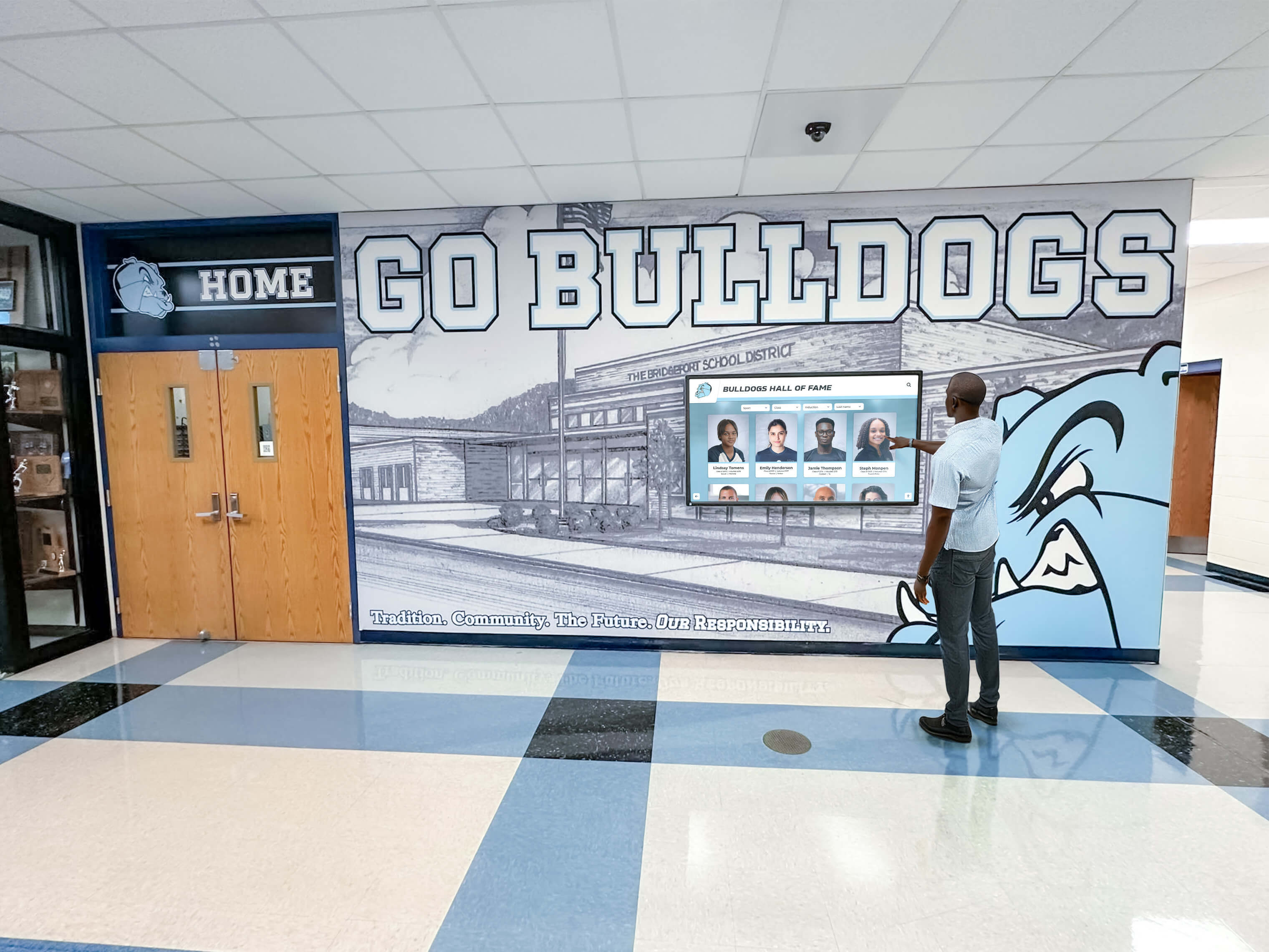

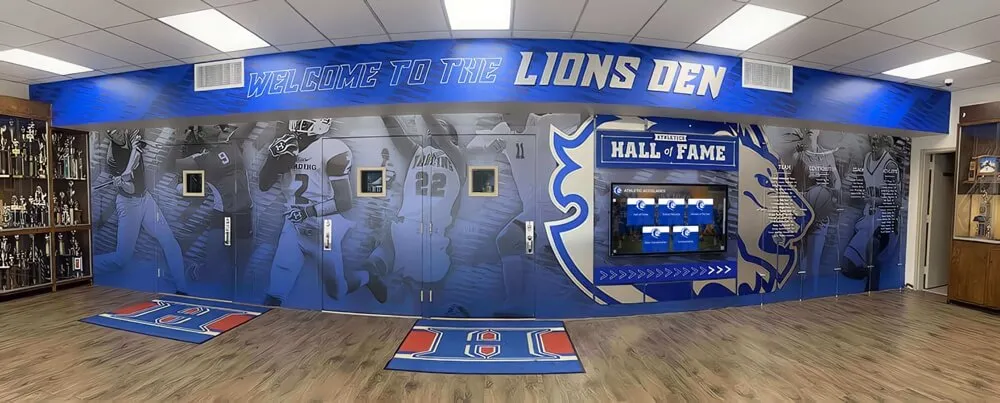
Intuitive interfaces enable self-service information access reducing staff workload while improving visitor experience
Integration with Broader Event Strategy
Touchscreen kiosks work most effectively as components of comprehensive event strategies rather than isolated technology implementations.
Staff-Assisted vs. Self-Service Approaches
Different event contexts and product complexity levels call for varying balances between automated and human interaction.
Pure Self-Service Models work well for straightforward products and high-traffic environments where staff availability limits individual attention. This approach maximizes staff efficiency by handling routine questions, operates effectively during busy periods when staff assist other visitors, provides consistent information delivery eliminating individual variation, captures visitor information and interests for follow-up, and enables 24/7 operation in showroom environments.
Self-service limitations include difficulty addressing complex custom requirements, lack of relationship building through conversation, challenges adapting to unexpected questions, and missing opportunities to read visitor interest and adjust approach.
Staff-Augmented Interactive Experiences use technology supporting rather than replacing human interaction. This hybrid approach enables staff to guide visitors through content, provides consistent information foundation for discussions, supports staff with specification details and technical data, demonstrates professionalism through technology investment, and facilitates transition from overview to detailed conversation.
Appropriate Model Selection depends on product complexity, target audience, staffing levels, and event format. Self-service emphasis suits high-traffic public events, straightforward products with clear differentiation, limited booth staffing, and primarily awareness-building objectives. Staff-augmented approaches serve complex technical products, solution-selling requiring customization, high-value enterprise sales, and relationship-focused business development.
Multi-Touchpoint Experience Design
Visitors interact with brands across multiple touchpoints before, during, and after events requiring consistent experience design.
Pre-Event Engagement uses digital channels building awareness and scheduling appointments. Effective pre-event tactics include email campaigns highlighting booth location and demonstrations, social media content previewing new products or announcements, website landing pages with event information, appointment scheduling systems reducing wait times, and preview content generating interest in full demonstrations.
At-Event Touchpoints create cohesive experiences across interaction methods. Coordinated touchpoints include booth signage and graphics matching digital content themes, printed materials complementing rather than duplicating digital content, staff conversations building on information available through kiosks, demonstration stations showing products mentioned in digital content, and seamless handoff between self-service exploration and staff assistance.
Post-Event Follow-Up continues conversations initiated through event interactions. Effective follow-up includes personalized emails referencing specific product interests, access to content explored during event, additional resources addressing unanswered questions, appointment scheduling for next-step conversations, and nurture campaigns maintaining engagement toward purchase decisions.
Interactive museum and gallery displays demonstrate multi-touchpoint experience design principles applicable to event environments where visitor engagement extends beyond single interactions.
Measuring Effectiveness and ROI
Understanding whether touchscreen investments deliver value requires establishing measurement frameworks tied to business objectives.
Engagement Metrics quantify how visitors interact with content. Valuable measurements include total interaction sessions and unique visitors, average session duration indicating engagement depth, popular content and navigation paths, completion rates for multi-step processes, return visitor rates showing repeated interest, and peak usage times informing staffing decisions.
Lead Generation and Quality connect interactions to sales pipeline. Important metrics include contact information capture rates, badge scans and visitor identification, stated product interests and application needs, requested follow-up or demonstrations, download behavior indicating serious interest, and ultimately conversion rates from event leads to opportunities and sales.
Content Performance Analysis identifies what information resonates with audiences. Useful insights include most-viewed product pages and features, search queries revealing visitor interests, comparison tool usage patterns, dropped interactions indicating confusing content, help or FAQ access suggesting information gaps, and session recordings revealing usability issues.
Cost-Benefit Analysis justifies investment through quantifiable returns. ROI calculations include technology cost (hardware, software, development), operational costs (maintenance, updates, connectivity), comparison to alternative lead generation costs, qualified lead volume and conversion value, staff efficiency improvements, and brand impression and awareness value.
Extending Event Technology to Permanent Installations
Technology developed for events often provides foundation for ongoing showroom, lobby, or facility installations extending value beyond temporary deployments.
Showroom and Facility Implementations
Permanent installations leverage event technology while adding capabilities supporting long-term operation.
Showroom Interactive Displays provide always-available product information for visitors during business hours and after. Permanent showroom systems benefit from reliable network connectivity enabling real-time content updates, integration with facility systems (lighting, security), extensive product catalogs beyond event-specific highlights, appointment scheduling and sales team notification, CRM integration capturing visitor information and interests, and sophisticated analytics tracking long-term patterns.
Reception and Lobby Installations serve visitors while reinforcing brand professionalism and innovation. Lobby applications include facility wayfinding and directory information, company history and achievement highlights, product portfolio overview, current promotion or announcement content, visitor check-in and appointment notification, and corporate social responsibility or community engagement content.
Training and Education Centers use interactive technology supporting customer and dealer training programs. Training applications include self-paced learning modules on product features, installation and maintenance procedures, troubleshooting and diagnostic guidance, certification programs with assessment, and reference libraries supporting ongoing learning.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions demonstrate extending similar technology platforms from event applications to permanent institutional recognition displays serving ongoing communication needs beyond temporary deployments.
Content Lifecycle and Maintenance
Long-term installations require sustainable content management processes preventing displays from becoming outdated and ignored.
Content Update Cadence establishes regular refresh preventing staleness. Effective schedules include daily rotation of featured products or promotions, weekly updates of news, announcements, or achievements, monthly refresh of product information and specifications, quarterly campaign and seasonal content changes, and annual comprehensive content review and overhaul.
Ownership and Responsibility assigns clear accountability for content quality. Sustainable structures identify content owners for different sections, establish approval workflows for changes, define update triggers (product launches, specifications changes), document style guidelines and standards, provide training on content management tools, and schedule regular content audits assessing quality and currency.
Technology Refresh Cycles maintain hardware and software currency. Appropriate planning includes display replacement every 5-7 years preventing failures, computing hardware refresh every 3-5 years maintaining performance, software platform updates for security and features, preventive maintenance schedules, and budget allocation for ongoing technology investment.
Emerging Trends and Future Considerations
Understanding developing technologies and changing user expectations helps plan investments that remain relevant beyond immediate event cycles.
Advanced Interaction Methods
Touch remains primary interaction method, but supplementary approaches address limitations and create novel experiences.
Voice and Conversational Interfaces enable hands-free information access and natural language queries. Voice applications suit busy environments where touch unavailable, support accessibility for vision or mobility limitations, enable complex questions in natural language, reduce learning curve for technology-averse users, and provide alternative interaction during high-traffic periods when touching shared surfaces concerns some users.
Voice interface limitations include ambient noise challenges in event environments, privacy concerns in public spaces, language and accent recognition variability, and content structure requirements supporting conversational interaction.
Gesture and Motion Recognition enable touch-free interaction through cameras tracking user movement. Gesture applications include attract mode activation when visitors approach, hands-free navigation through swipe gestures, accessibility features supporting users unable to touch screens, hygiene considerations in health-conscious environments, and novel engagement creating memorable experiences.
Mobile Device Integration treats visitor smartphones as companion interfaces rather than competing platforms. Mobile integration approaches include QR codes triggering content continuation on personal devices, app-based interaction controlling larger displays, personal device content creation (photos, preferences) appearing on shared screens, takeaway information sent to phones for later review, and appointment or contact information capture through mobile forms.
Artificial Intelligence and Personalization
AI capabilities enable more sophisticated content adaptation and visitor understanding while raising implementation and privacy considerations.
Content Recommendation Engines suggest relevant information based on interaction patterns. Recommendation systems include products matching expressed interests or viewed items, related content supporting logical information flow, application examples relevant to visitor industry or use case, and next-step guidance toward deeper engagement or contact.
Natural Language Processing interprets complex questions enabling sophisticated search and guidance. NLP applications include conversational search interfaces accepting natural queries, FAQ systems understanding question intent, chatbot support providing automated assistance, and content summarization extracting key information.
Computer Vision and Audience Analytics anonymously analyze visitor demographics and engagement without identifying individuals. Vision applications include attention tracking identifying engaging vs. ignored content, crowd analytics informing staffing and demo scheduling, age and gender estimation enabling demographic analysis, and emotion recognition assessing content reaction.
Privacy considerations require clear disclosure of data collection, appropriate anonymization preventing identification, policy compliance (GDPR, CCPA), user consent where required, and data minimization collecting only necessary information.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Growing environmental awareness influences technology choices and operational approaches.
Energy Efficiency reduces operational cost and environmental impact. Efficient approaches include display power management with automatic sleep modes, LED backlighting reducing energy consumption vs. older technology, efficient computing platforms minimizing power draw, and solar or battery options for certain applications.
Circular Economy and Equipment Lifecycle extends value while reducing waste. Sustainable practices include modular designs supporting repair and component upgrade, display refurbishment and resale when replacing, responsible recycling through certified programs, and hardware selection favoring manufacturers with take-back programs.
Reduced Physical Materials shifts print-dependent information to digital delivery. Environmental benefits include reduced printed collateral and specification sheets, digital literature delivery via email or download, on-demand printing only when requested, and reusable rather than disposable event materials.
Implementation Roadmap for Equipment Manufacturers
Moving from concept to operational touchscreen systems requires structured planning addressing technical, content, and organizational considerations.
Needs Assessment and Requirements Definition
Successful implementations begin with clear understanding of objectives, audiences, and constraints guiding appropriate solution design.
Objective Clarification establishes what success looks like. Essential questions include primary goals (lead generation, education, brand awareness), key performance indicators and measurement approaches, audience priorities (technical experts vs. general public), event types and environments where systems deploy, and content update frequency and ownership.
Technical Requirements Gathering defines capabilities and constraints. Important specifications include supported platforms (web, iOS, Android, dedicated kiosks), offline operation requirements, network dependency and connectivity approaches, integration needs (CRM, marketing automation, analytics), security and data privacy requirements, and budget parameters for development and ongoing operation.
Content Audit and Gap Analysis determines what exists and what must be created. Audit components include inventory of existing product information and media, assessment of format and quality for digital use, identification of content gaps requiring creation, evaluation of competitor approaches for benchmark, and documentation of technical depth requirements.
Development and Implementation Phases
Structured implementation prevents common failures while establishing foundation for long-term success.
Phase 1: Prototype and Core Content establishes technical foundation and initial content. Initial scope includes platform selection and architecture design, core navigation and interface development, essential product information for highest-priority products, basic interactive features (search, compare, contact), and internal testing with stakeholder feedback.
Phase 2: Expansion and Refinement builds on prototype adding breadth and depth. Expansion includes additional product coverage and content types, advanced interactive tools (configurators, calculators), multimedia content (videos, 3D models), mobile and cross-platform optimization, and initial event deployment for real-world testing.
Phase 3: Integration and Optimization connects systems to broader technology ecosystem. Integration includes CRM and marketing automation connections, analytics implementation and dashboard creation, content management workflow establishment, staff training program development, and performance optimization based on usage data.
Phase 4: Scale and Evolution extends capability and deployment. Scaling includes deployment across event program, permanent showroom and facility installations, continuous content expansion and updates, feature enhancement based on user feedback, and regular technology refresh maintaining currency.
Organizational Change Management
Technology adoption requires addressing human and organizational factors beyond technical implementation.
Stakeholder Engagement builds support across affected groups. Engagement approaches include early involvement of sales and marketing teams, demonstration of benefits through prototypes, addressing concerns about changing processes, training programs building competence and confidence, and feedback mechanisms enabling continuous improvement.
Process Documentation establishes sustainable operations. Essential documentation includes content creation and approval workflows, update scheduling and responsibility assignments, troubleshooting procedures and support contacts, best practices for event deployment, and success measurement and reporting approaches.
Continuous Improvement Culture maintains system relevance and effectiveness. Improvement practices include regular usage data review and analysis, user feedback collection and response, competitive benchmark monitoring, technology trend assessment, and experimentation with new features and approaches.

Natural touch interactions create intuitive user experiences requiring minimal instruction or assistance
Conclusion: Transforming Product Communication Through Interactive Technology
Touchscreen kiosks at events and functions represent significant opportunities for equipment manufacturers to communicate product value more effectively than traditional static displays and manual demonstrations allow. When properly designed and implemented, interactive technology creates self-guided exploration experiences adapting to visitor knowledge levels and interests while maintaining consistent information quality regardless of staff availability or expertise.
The most effective implementations recognize that touchscreen technology serves broader communication strategy rather than existing as isolated point solutions. Successful systems work consistently across websites, mobile devices, and physical installations at events, creating unified experiences that begin with pre-event digital engagement, continue through self-service and staff-assisted booth interactions, and extend into post-event follow-up maintaining momentum toward business relationships and sales conversions.
Moving from concept to operational systems requires addressing technical platform selection, content strategy and creation, interface design, event-specific implementation considerations, integration with broader marketing technology, and organizational change management ensuring sustained use and improvement. Equipment manufacturers willing to invest in comprehensive approaches rather than minimal implementations realize differentiation advantages through enhanced visitor engagement, improved lead quality, reduced staff workload, and professional brand positioning that technology investment signals.
Ready to Transform Your Event Presence?
Discover how comprehensive touchscreen solutions from Rocket Alumni Solutions can help you create engaging product demonstration experiences that work seamlessly across events, websites, and permanent installations. Our platforms combine intuitive interfaces, flexible content management, and robust analytics designed for equipment manufacturers and institutional organizations showcasing complex products and achievements.
Explore Interactive SolutionsStarting Your Touchscreen Journey
Organizations beginning touchscreen implementation should prioritize clear objective definition establishing what success means, audience understanding identifying who will use systems and what they need, existing content audit determining what you have and what requires creation, realistic budget allocation for both development and ongoing operation, and phased approach starting with core functionality before expanding to advanced features.
This measured approach prevents overwhelming scope while establishing working systems demonstrating value and building organizational confidence supporting continued investment and expansion.
The Competitive Advantage of Interactive Technology
In crowded event environments where hundreds of exhibitors compete for limited visitor attention, interactive touchscreen technology differentiates sophisticated exhibitors from competitors relying on printed brochures and traditional conversations. Self-service exploration appeals to visitors uncomfortable with aggressive sales approaches while capturing valuable data about interests and intent that traditional conversations miss unless staff diligently record every detail.
Beyond immediate event applications, technology developed for temporary deployments extends to permanent showroom installations, facility lobby displays, training centers, and customer experience centers creating ongoing value from development investments while maintaining consistent brand experiences across all customer touchpoints. Equipment manufacturers ready to move beyond traditional event presence should assess their current approaches against opportunities interactive technology creates, then systematically build capabilities through measured implementation supporting immediate event needs while establishing platforms for expanded application.
The difference between effective and underutilized touchscreen systems typically stems not from technology selection but from comprehensive planning addressing technical, content, design, and organizational factors together rather than treating each as isolated concern. Your event presence and product communication represent valuable brand touchpoints—strategic interactive technology investment transforms these opportunities from forgettable booth visits into engaging experiences that visitors remember, understand, and act upon long after events conclude.
Ready to explore touchscreen solutions? Learn about digital signage content strategies, discover touchscreen display design principles, or talk to our team about implementing engaging interactive experiences tailored to your products, audiences, and event requirements.