Choosing the right screen for digital signage fundamentally determines display effectiveness, operational costs, viewer experience, and long-term return on investment. Whether you’re implementing recognition displays for educational institutions, wayfinding systems for public facilities, menu boards for restaurants, or promotional displays for retail environments, understanding the full spectrum of available screen technologies—from traditional LCD and LED to cutting-edge OLED and MicroLED—enables informed decisions matching technical specifications to specific application requirements.
The digital signage display market offers dozens of screen technologies, each with distinct advantages regarding brightness levels, contrast ratios, viewing angles, power consumption, lifespan expectations, and price points. Making optimal selections requires understanding not just marketing terminology, but fundamental differences in how various display technologies produce images, handle ambient lighting, withstand environmental conditions, and perform across years of continuous commercial operation.
Organizations implementing digital signage commonly face confusion navigating technical specifications, manufacturer claims, and conflicting recommendations from vendors each promoting their preferred technologies. This comprehensive guide cuts through the complexity by examining every major screen type currently used for digital signage applications, explaining technical specifications in practical terms, comparing technologies across relevant criteria, and providing application-specific recommendations that match screen capabilities to real-world deployment requirements.
Digital signage screens have evolved dramatically over the past decade, progressing from heavy cathode ray tube (CRT) displays to slim liquid crystal displays (LCDs), bright light-emitting diode (LED) panels, stunning organic LED (OLED) screens, and emerging technologies like MicroLED and transparent displays. Each technological advancement addresses specific limitations while introducing new capabilities that expand what digital signage can accomplish in diverse environments from bright outdoor locations to controlled indoor spaces.

Modern digital signage installations often combine multiple screen types to create impactful visual communication systems
Understanding Digital Signage Display Fundamentals
Before examining specific screen technologies, understanding key technical concepts and specifications helps evaluate manufacturer claims and compare options objectively across different display types.
Key Display Specifications Explained
Resolution and Pixel Density
Display resolution indicates the total number of pixels (picture elements) a screen contains, typically expressed as horizontal pixels by vertical pixels. Common digital signage resolutions include Full HD (1920×1080 pixels), 4K or Ultra HD (3840×2160 pixels), and 8K (7680×4320 pixels) for premium applications. Higher resolutions enable sharper text, more detailed images, and closer viewing distances without visible pixelation.
Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), determines image sharpness at specific viewing distances. A 55-inch Full HD display provides approximately 40 PPI, while a same-sized 4K display delivers 80 PPI—significantly sharper for close viewing applications. Digital signage applications requiring text readability from 3-6 feet benefit substantially from 4K resolution, while displays viewed from 15+ feet may show minimal visual improvement from resolutions beyond Full HD.
Brightness and Nits
Display brightness, measured in nits (candelas per square meter), determines screen visibility in ambient lighting conditions. Indoor digital signage typically requires 300-700 nits depending on ambient lighting, while outdoor applications need 1,500-5,000+ nits to remain visible in direct sunlight. According to display industry research, brightness represents the single most important specification for outdoor digital signage effectiveness.
Many consumer televisions provide 250-400 nits brightness—adequate for controlled home lighting but insufficient for many commercial applications with bright ambient light from windows or overhead lighting. Commercial-grade digital signage displays specifically address this limitation with brightness levels 2-4 times higher than consumer equivalents.
Contrast Ratio and Dynamic Range
Contrast ratio expresses the difference between the brightest white and darkest black a display can produce, written as ratios like 3000:1 or 5000:1. Higher contrast ratios produce more vivid images with greater depth and visual impact. Static contrast ratio measures performance displaying a pure black screen versus pure white screen, while dynamic contrast ratio measures performance adjusting backlight intensity—a specification often inflated in marketing materials.
High dynamic range (HDR) technology expands the range of colors and luminosity displays can reproduce, creating more realistic images with greater detail in both bright and dark areas. HDR capability proves particularly valuable for digital signage showcasing photography, video content, or product imagery where color accuracy and visual impact drive engagement.

Commercial-grade displays provide the brightness, contrast, and reliability necessary for continuous operation in public environments
Viewing Angles
Viewing angle specifications indicate how far off-center viewers can observe displays before experiencing significant brightness loss or color shift. Specifications list horizontal and vertical viewing angles, typically ranging from 160-178 degrees for quality displays. Digital signage installations where viewers approach from multiple directions—lobby displays, directional signage, wayfinding kiosks—require wide viewing angles ensuring consistent image quality regardless of viewer position.
LCD technology historically struggled with viewing angle performance compared to alternative technologies, though modern IPS (In-Plane Switching) LCD panels largely address this limitation. OLED displays provide exceptional viewing angles approaching 180 degrees with minimal color shift or brightness loss at extreme angles.
Refresh Rate and Response Time
Refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates how many times per second a display updates its image. Standard displays operate at 60Hz, while high-performance displays support 120Hz or higher. For most digital signage applications displaying static or slow-moving content, 60Hz proves entirely adequate. Applications incorporating significant motion—sports highlights, action videos, interactive games—benefit from higher refresh rates producing smoother motion.
Response time measures how quickly pixels can change colors, expressed in milliseconds. Lower response times (typically 5-8ms for quality displays) prevent motion blur and ghosting effects during fast content changes. Static digital signage displaying primarily images and text tolerate slower response times, while video-intensive applications require faster pixel response.
LCD Display Technology for Digital Signage
Liquid crystal display (LCD) technology remains the most common screen type for indoor digital signage applications, offering proven reliability, reasonable costs, and mature technology with standardized manufacturing across numerous suppliers.
How LCD Displays Work
LCD screens sandwich liquid crystals between two polarized glass layers with a backlight providing illumination. Electrical currents control how liquid crystals align, determining how much backlight passes through each pixel to create images. Color filters produce red, green, and blue subpixels that combine to generate the full color spectrum viewers perceive.
Traditional LCD displays use Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp (CCFL) backlighting, though modern implementations predominantly use LED backlighting—technically making these LCD displays “LED-backlit LCD” panels. The term “LED display” in digital signage contexts typically refers to LED-backlit LCD screens rather than true direct-view LED panels (discussed separately below).
LCD Panel Technologies: TN, VA, and IPS
Three primary LCD panel types serve digital signage applications, each with distinct performance characteristics affecting suitability for specific uses.
TN (Twisted Nematic) Panels
TN panels represent the oldest and least expensive LCD technology, offering fast response times but limited viewing angles (typically 140-160 degrees) and inferior color reproduction compared to alternatives. Digital signage applications rarely use TN panels except in budget-constrained implementations where viewing occurs primarily straight-on and color accuracy matters less than cost.
VA (Vertical Alignment) Panels
VA panels provide superior contrast ratios (typically 3000:1 to 5000:1) compared to IPS alternatives, producing deeper blacks and more vivid images. Viewing angles (typically 160-178 degrees) fall between TN and IPS performance. Response times, while improved in modern VA panels, remain slower than TN technology, potentially causing motion blur in fast-moving content.
Digital signage applications prioritizing contrast and image depth—particularly environments with controlled lighting where deep blacks enhance visual impact—benefit from VA panel technology. Many commercial digital signage displays targeting general indoor applications use VA panels balancing performance and cost effectively.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) Panels
IPS panels deliver the best viewing angles (typically 178 degrees horizontal and vertical) and most accurate color reproduction, making them ideal for digital signage viewed from multiple positions or applications requiring color accuracy. IPS contrast ratios (typically 1000:1 to 3000:1) lag behind VA technology, though this limitation rarely matters for typical signage applications.
Premium digital signage implementations, interactive touchscreen displays, and applications requiring color-critical content reproduction typically specify IPS panels despite marginally higher costs compared to VA alternatives.
LCD Advantages for Digital Signage
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
LCD technology’s maturity and widespread manufacturing create competitive pricing across numerous vendors and screen sizes. Organizations can source LCD displays from dozens of manufacturers at every price point from budget to premium, ensuring competitive procurement regardless of project scale or requirements.
Proven Reliability
Decades of commercial LCD deployment demonstrate reliable performance with typical lifespans of 50,000-100,000 hours (5.7-11.4 years of continuous 24/7 operation) before brightness degrades to 50% of original levels. This proven longevity provides confidence in total cost of ownership calculations and reduces replacement frequency compared to emerging technologies with less extensive operational history.
Wide Size Range
LCD manufacturing supports screen sizes from small 10-inch tablets through massive 98-inch commercial displays, providing flexibility for diverse digital signage applications. This comprehensive size availability enables organizations to select optimal screen sizes for viewing distances and installation spaces without technology constraints limiting options.

LCD displays serve effectively in controlled indoor environments with appropriate brightness for ambient lighting conditions
LCD Limitations and Considerations
Brightness Constraints
Even the brightest commercial LCD displays struggle in high ambient light environments, particularly outdoor applications or indoor spaces with significant natural light. While premium commercial LCDs achieve 700-1,000 nits brightness, this performance falls short of the 2,000-5,000+ nits required for outdoor visibility in direct sunlight.
Organizations implementing digital signage in bright environments must either accept reduced visibility during peak ambient light conditions, implement physical shading solutions, or select alternative display technologies specifically designed for high-brightness applications.
Backlight Uniformity and Edge Bleeding
LCD backlighting occasionally produces visible brightness variations across screen areas, particularly noticeable displaying solid colors or dark scenes. Lower-cost displays exhibit more pronounced uniformity issues, while premium models implement advanced backlighting systems minimizing these effects.
Edge bleeding—where backlight leaks through LCD panel edges causing bright areas during dark content—affects some LCD displays, particularly older or budget models. Organizations should evaluate actual display samples rather than relying solely on specifications to assess backlight performance for specific signage content.
Direct-View LED Display Technology
Direct-view LED displays, fundamentally different from LED-backlit LCD panels, use arrays of individual light-emitting diodes as both light source and image-forming elements. These true LED displays dominate large-format outdoor digital signage and video wall applications where extreme brightness, massive sizes, and pixel-level dimming provide advantages LCD technology cannot match.
LED Display Architecture and Pixel Pitch
Direct-view LED displays consist of LED modules containing red, green, and blue LED chips forming individual pixels. Pixel pitch—the center-to-center distance between adjacent pixels measured in millimeters—determines resolution and optimal viewing distance. Common pixel pitches range from 0.9mm for close-viewing applications to 10mm+ for outdoor billboards viewed from hundreds of feet away.
Calculating optimal viewing distance from pixel pitch follows the general rule: viewing distance (in feet) equals pixel pitch (in millimeters) multiplied by 8-10. A 2.5mm pixel pitch LED display provides sharp images from approximately 20-25 feet, while a 10mm pitch display requires 80-100 foot viewing distances to appear sharp rather than visibly pixelated.
Unlike fixed-size LCD panels, LED displays scale to virtually unlimited dimensions by tiling LED modules together, enabling massive video walls and outdoor displays impossible with other technologies. This modular architecture also simplifies repairs—technicians replace individual failed modules rather than entire displays, reducing service costs and downtime.
Advantages of Direct-View LED Displays
Extreme Brightness Capability
LED displays achieve brightness levels of 1,500-10,000+ nits, remaining clearly visible even in direct sunlight. This extreme brightness capability makes LED technology the dominant choice for outdoor digital signage including highway billboards, building-mounted displays, outdoor stadium screens, and street-level advertising displays where ambient light levels would render LCD screens invisible.
Indoor LED video walls can adjust brightness lower for comfortable viewing while maintaining capability for high-impact content when desired. This brightness range flexibility proves valuable for applications requiring visibility across varying ambient lighting conditions throughout the day.
Unlimited Size Scalability
LED’s modular architecture enables displays limited only by structural support and budget constraints. Organizations regularly implement LED video walls spanning 20-50+ feet horizontally, creating immersive visual experiences impossible with fixed-size LCD panels. Large-format applications including arena and stadium displays, corporate lobby installations, and event venue screens leverage LED’s unique scalability advantage.
True Black Levels and Contrast
Unlike LCD technology requiring backlight management, LED pixels simply turn off to produce perfect blacks with zero light emission. This capability creates exceptional contrast ratios (often specified as infinite contrast or 10,000:1+) with dramatic visual impact particularly noticeable in dark environments like theaters, concert venues, or nighttime outdoor applications.
Per-pixel brightness control enables LED displays to optimize image quality across the entire brightness spectrum simultaneously—bright highlights and deep shadows within the same frame—providing HDR performance superior to most LCD implementations.

LED displays excel in applications requiring high brightness, large formats, or modular configurations scaling beyond standard panel sizes
Direct-View LED Limitations
Cost Considerations
Direct-view LED displays cost significantly more than LCD alternatives—typically 3-10 times higher per square foot depending on pixel pitch and specifications. Small fine-pitch LED displays can cost $20,000-$100,000+ compared to $1,000-$5,000 for equivalent-sized LCD panels. This substantial price premium limits LED adoption primarily to applications where extreme brightness, massive size, or modular architecture justify the investment.
Organizations should carefully evaluate whether LED’s unique capabilities actually benefit specific applications or if less expensive LCD alternatives deliver adequate performance at dramatically lower costs.
Resolution and Viewing Distance Constraints
Fine pixel pitch LED technology continues improving, with sub-1mm pitches now available enabling closer viewing distances. However, achieving pixel densities matching 4K LCD panels requires expensive ultra-fine-pitch LED implementations still uncommon in typical signage applications.
Applications requiring text readability from close viewing distances or detailed image reproduction generally favor high-resolution LCD technology over coarser-pitch LED alternatives unless extreme brightness or size requirements override resolution considerations.
Power Consumption
LED displays consume significantly more power than LCD alternatives—often 2-5 times higher depending on content brightness and display size. Large outdoor LED displays may draw tens of kilowatts during operation, creating substantial ongoing electricity costs beyond initial acquisition expenses.
Organizations implementing large LED displays should calculate total cost of ownership including electricity expenses that may exceed $5,000-$20,000 annually for large-format installations operating continuously.
OLED Display Technology
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) displays represent advanced technology where organic compounds emit light when electrical current passes through them, eliminating backlighting entirely. Each pixel generates its own light, enabling displays to turn off individual pixels completely for perfect blacks and exceptional contrast ratios.
OLED Technical Advantages
Superior Image Quality
OLED technology delivers image quality advantages including infinite contrast ratios with true blacks (0 nits) adjacent to bright whites, exceptional color accuracy and saturation, 178-degree viewing angles with minimal color shift, and fast pixel response times (typically under 1ms) eliminating motion blur.
This combination of visual performance characteristics creates stunning images with depth and vibrancy that immediately differentiate OLED displays from LCD alternatives. Premium digital signage applications where image quality directly impacts viewer engagement and brand perception increasingly specify OLED technology despite higher costs.
Thin and Flexible Form Factors
OLED’s self-emissive architecture eliminates bulky backlighting systems, enabling displays as thin as 2-4mm—approximately one-third the depth of equivalent LCD panels. This slim profile enables mounting flush against walls, integrating into architectural elements, or creating transparent display installations impossible with thicker technologies.
Some OLED implementations use flexible substrates enabling curved displays, rollable screens, and unconventional form factors that expand creative possibilities for digital signage in retail, museums, and experiential marketing applications.
OLED Limitations for Digital Signage
Brightness Limitations
While OLED provides exceptional contrast and black levels, maximum brightness typically ranges only 400-1,000 nits—lower than many commercial LCD displays and far below LED technology. This brightness limitation restricts OLED primarily to controlled indoor environments with moderate ambient lighting.
Outdoor OLED digital signage remains impractical due to insufficient brightness competing with sunlight. High ambient light indoor environments—near windows or under bright overhead lighting—may also challenge OLED visibility compared to brighter LCD or LED alternatives.
Cost and Availability
OLED displays cost substantially more than equivalent LCD panels, with price premiums of 2-5 times common depending on size and specifications. Limited manufacturing capacity compared to LCD’s massive global production further constrains availability, particularly for large commercial display sizes.
While OLED smartphone displays have become mainstream and medium-size consumer OLED TVs increasingly common, large-format commercial OLED displays suitable for digital signage remain premium products with limited vendor options and higher costs restricting adoption primarily to high-budget implementations.
Burn-in and Lifespan Concerns
OLED displays risk image retention or permanent “burn-in” when static content elements remain on screen for extended periods—a significant concern for digital signage frequently displaying logos, graphics, or interface elements in fixed positions. While manufacturers implement various burn-in mitigation technologies, the risk remains particularly relevant for 24/7 signage applications.
OLED lifespan, while improving, generally trails LCD technology. Manufacturers typically specify 30,000-50,000 hours to 50% brightness—adequate for typical digital signage but shorter than LCD’s 50,000-100,000 hour ratings. Organizations implementing OLED signage should plan replacement schedules acknowledging shorter operational lifespans compared to mature LCD technology.
Emerging Display Technologies for Digital Signage
Beyond established LCD, LED, and OLED technologies, several emerging display innovations provide unique capabilities for specialized digital signage applications.
MicroLED Technology
MicroLED displays combine direct-view LED technology’s benefits—high brightness, excellent contrast, unlimited scalability—with pixel sizes small enough to achieve resolutions approaching LCD panels. Individual microscopic LEDs (typically under 100 micrometers) form pixels without organic materials used in OLED, providing OLED-like visual quality with LED’s superior brightness and longevity.
Current MicroLED Status
MicroLED technology remains in early commercial stages with extremely high costs limiting adoption primarily to flagship installations in premium retail, luxury hospitality, and corporate headquarters where cutting-edge technology showcases organizational innovation regardless of price. As manufacturing scales over coming years, industry analysts project MicroLED costs declining sufficiently for broader digital signage adoption in premium applications.
MicroLED’s combination of LCD-like resolution, LED brightness, OLED contrast, and long operational lifespan positions the technology as potentially transformative for digital signage once manufacturing advances reduce costs to commercially viable levels for typical applications.

Emerging display technologies enable new form factors and performance levels expanding digital signage creative possibilities
Transparent LED and LCD Displays
Transparent displays enable viewing through screens to objects or environments behind them, creating unique opportunities for storefront windows, museum cases, and architectural installations where signage should not obstruct sight lines.
Transparent LED
Transparent LED displays use sparse LED grids with substantial space between pixels, allowing light transmission through the display. Transparency levels typically range from 60-90% depending on pixel density and brightness requirements. These displays excel for storefront installations maintaining window shopping visibility while presenting digital content, or glass partition applications in corporate environments.
Lower resolution compared to standard LED displays (due to reduced pixel density maintaining transparency) limits content complexity, favoring large graphics, text, and simple videos over detailed imagery requiring fine resolution.
Transparent LCD
Transparent LCD panels remove the backlight and rear polarizing layer of traditional LCD displays, allowing light transmission through pixels when displaying bright content. Transparency typically achieves 10-15%—significantly lower than LED alternatives—with dimmer overall image brightness limiting applications primarily to controlled lighting environments.
While transparent LCD costs less than transparent LED alternatives, lower transparency and brightness restrict practical applications compared to LED technology better suited to transparent display requirements.
E-Paper and E-Ink Displays
Electronic paper displays, commonly called e-ink displays, use microcapsule technology reflecting ambient light rather than emitting light like LCD or LED screens. This architecture creates paper-like appearance with exceptional sunlight readability while consuming power only during image updates, not static display.
E-Paper Advantages
Digital signage applications benefiting from e-paper technology include ultra-low power consumption (displays maintain images indefinitely without power), excellent outdoor readability without requiring high brightness, wide viewing angles approaching printed materials, and thin, lightweight form factors.
E-paper displays prove ideal for digital directory systems, price tags, transit schedules, building directories, and menu boards where content updates infrequently and power availability limits LCD or LED alternatives.
E-Paper Limitations
Slow refresh rates (typically 1-2 seconds full screen update) make e-paper unsuitable for video or frequently changing content. Limited color reproduction with most implementations offering only grayscale, and increasingly capable but still limited color e-paper options restrict creative possibilities compared to vibrant LCD or LED displays.
Organizations implementing e-paper should recognize technology’s specific strengths—low power, readability, static content—rather than attempting applications better suited to traditional display technologies.
Projection Displays
Digital projectors create large-format displays by projecting light onto screens or surfaces rather than using self-contained display panels. While technically not digital signage “screens,” projection technology serves similar applications in specific environments.
When Projection Makes Sense
Projection displays provide advantages for applications requiring extremely large images (10+ feet diagonal), temporary or movable displays, unusual aspect ratios or screen shapes, and lower cost per square foot for very large displays compared to modular LED alternatives.
Projection works effectively in controlled environments with low ambient light—theaters, auditoriums, conference rooms—where light levels accommodate projector brightness limitations. Outdoor projection or high ambient light applications generally prove impractical without expensive high-brightness projectors or significant light control measures.
Projection Limitations
Projectors require ambient light control to maintain image visibility, making them unsuitable for many digital signage environments with unchangeable lighting conditions. Regular maintenance including filter cleaning and lamp replacement (typically 2,000-5,000 hours) creates ongoing operational requirements exceeding self-contained displays.
Short-throw and ultra-short-throw projectors minimize required projection distance, enabling large images in constrained spaces where traditional projectors wouldn’t fit. These specialized projectors cost significantly more than standard models but expand projection viability for certain space-limited applications.
Screen Size Considerations for Digital Signage
Selecting appropriate display sizes requires understanding viewing distance relationships, content type requirements, installation space constraints, and budget considerations that together determine optimal screen specifications.
Viewing Distance and Screen Size Relationship
Industry guidelines suggest minimum viewing distances of 1.5-2.5 times screen diagonal for comfortable viewing without perceiving individual pixels on standard resolution displays. A 55-inch display requires minimum viewing distance of approximately 7-11 feet for Full HD resolution, while 4K resolution enables closer viewing (approximately 4-7 feet) before pixelation becomes apparent.
Maximum viewing distance depends on content type—text requires closer viewing for readability than images or video that remain recognizable from greater distances. Organizations should design digital signage placement and size around the audience’s actual viewing distances in specific installation locations rather than arbitrary size preferences.
Common Digital Signage Screen Sizes
Small Format (10-32 inches)
Small displays serve desktop applications, individual workstation signage, point-of-sale terminals, tablet-based interactive displays, and shelf-edge retail signage where viewing occurs from immediate proximity (1-4 feet) and space constraints limit larger options.
These compact displays typically use consumer-grade panels rather than commercial specifications, providing adequate performance for limited-hours operation in controlled environments but potentially lacking durability for demanding commercial use.
Medium Format (43-55 inches)
Medium displays represent the most common digital signage category, serving lobby displays, hallway signage, directional wayfinding, menu boards, and general indoor applications where viewers typically observe from 6-15 feet. This size range offers optimal balance of visibility, cost-effectiveness, and physical space requirements for typical commercial environments.
Commercial-grade panels in this size category provide extensive options across all major technologies (LCD, LED, OLED) with competitive pricing and broad vendor availability simplifying procurement and ensuring long-term product availability for standardized deployments.
Large Format (65-98 inches)
Large displays create impactful presentations in lobbies, auditoriums, retail flagship locations, transportation hubs, and corporate environments where viewer distances exceed 15 feet or visual impact justifies premium investments. These displays cost significantly more than medium formats—typically $3,000-$15,000+ depending on technology and specifications—limiting deployment primarily to prominent locations where size delivers meaningful impact.
Manufacturing complexity increases at larger sizes, reducing vendor options and potentially extending lead times compared to mainstream medium-format displays. Organizations should verify actual product availability and realistic delivery schedules rather than assuming all advertised sizes ship immediately from stock.
Extra-Large and Video Walls
Applications requiring displays beyond single-panel limits (98+ inches diagonal) typically implement video wall configurations tiling multiple displays or modular LED installations scaling to virtually unlimited dimensions. Video walls enable massive displays for arenas, stadiums, broadcast studios, control rooms, retail flagships, and corporate showcase installations.
Video wall implementations require specialized mounting systems, careful calibration for uniform appearance across panels, and often dedicated video wall controllers managing content distribution across multiple displays. These requirements increase implementation complexity and costs beyond simple single-display installations.

Strategic screen sizing ensures optimal visibility and readability from actual viewing distances in specific installation environments
Indoor vs. Outdoor Digital Signage Screen Requirements
Environmental conditions dramatically influence display technology selection, with outdoor applications imposing requirements far exceeding typical indoor specifications.
Outdoor Digital Signage Requirements
Brightness and Sunlight Readability
Outdoor visibility requires displays achieving 2,000-5,000+ nits brightness depending on sun exposure and viewing conditions. Direct sunlight produces 5,000-10,000 nits illumination, requiring high-brightness displays to maintain adequate contrast ratios for viewable images. Partially shaded locations may tolerate 1,500-2,500 nit displays, while full shade environments can function with 1,000-1,500 nits—still 2-3 times brighter than typical indoor commercial displays.
Display manufacturers specifically design outdoor-rated displays with brightness specifications far exceeding indoor models. Organizations should never attempt outdoor deployment of standard indoor displays expecting acceptable results—insufficient brightness will render screens virtually invisible in daylight regardless of content quality.
Environmental Protection and IP Ratings
Outdoor displays require weather sealing protecting internal electronics from moisture, dust, temperature extremes, and environmental contaminants. IP (Ingress Protection) ratings specify enclosure protection levels, with outdoor digital signage typically requiring IP65 or higher ratings indicating complete dust protection and protection against water jets from any direction.
Beyond waterproofing, outdoor displays implement temperature regulation systems maintaining operational temperature ranges despite external conditions potentially spanning -40°F to 120°F+ in extreme climates. Active cooling systems, insulation, and sometimes heating elements ensure reliable operation year-round in diverse geographic locations.
Vandalism and Impact Resistance
Public outdoor locations expose displays to vandalism risks requiring protective glazing significantly stronger than standard glass used in indoor displays. Tempered glass, polycarbonate shields, or specialized coatings protect display surfaces from impacts, scratches, and deliberate damage attempts common in unsecured public spaces.
Secure mounting systems prevent theft or unauthorized removal while providing maintenance access for authorized service personnel. The physical security requirements and ruggedized construction necessary for outdoor deployment contribute significantly to the 2-4x cost premium outdoor displays command over indoor equivalents.
Indoor Digital Signage Considerations
Ambient Light Management
While indoor environments eliminate outdoor’s extreme brightness requirements, ambient lighting conditions still significantly impact display visibility. Spaces with extensive windows or skylights require displays providing 500-1,000 nits brightness, while interior locations with controlled lighting operate effectively with 300-500 nit displays.
Organizations should assess actual ambient lighting conditions in specific installation locations—preferably using light meters measuring illumination levels—rather than making assumptions about “typical” indoor brightness requirements. Windows, skylights, and bright overhead lighting create localized high-brightness zones requiring displays beyond standard indoor specifications.
Operating Hours and Commercial Ratings
Digital signage operating 12-16+ hours daily requires commercial-grade displays specifically designed for extended operation rather than consumer TVs rated for typical residential use (4-6 hours daily average). Commercial displays implement enhanced cooling systems, higher-quality components, and design specifications enabling reliable 24/7 operation across years without premature failure.
The cost difference between consumer and commercial displays—typically 1.5-3x higher for commercial specifications—proves justified by extended lifespan and reduced failure rates that significantly impact total cost of ownership across multi-year deployment periods.
Installation and Mounting Flexibility
Indoor displays support diverse mounting options including wall mounting with flush or tilted brackets, floor stands for portable or temporary installations, ceiling mounting for overhead viewing, and custom integration into architectural elements, furniture, or specialized enclosures.
Organizations should specify mounting requirements during display selection ensuring chosen displays provide appropriate mounting patterns (VESA standard or custom), weight specifications, and ventilation requirements compatible with planned installation approaches. Some display technologies—particularly large LED video walls—impose substantial weight and structural requirements exceeding typical wall-mounting capabilities.
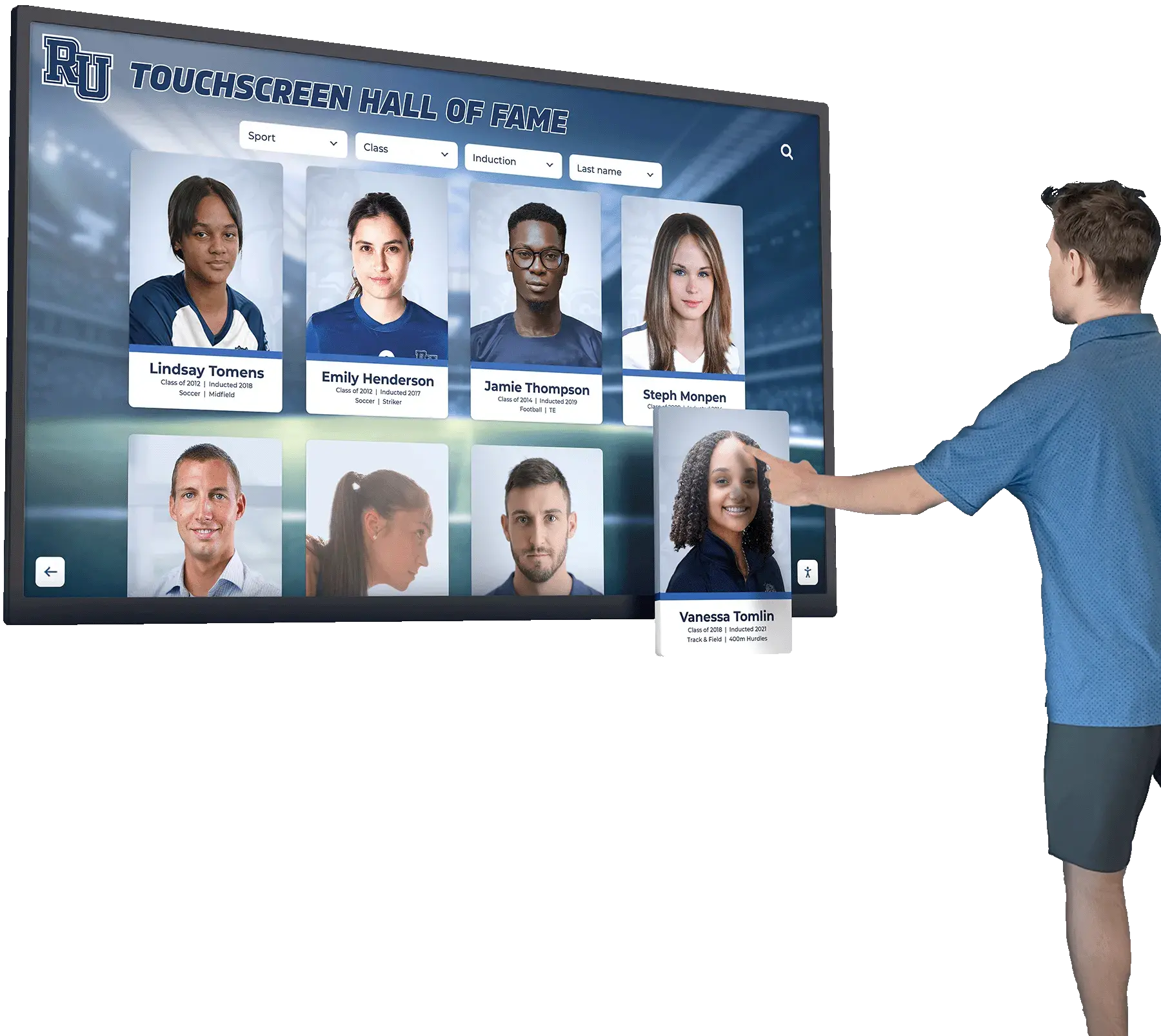
Interactive Touchscreen Displays for Digital Signage
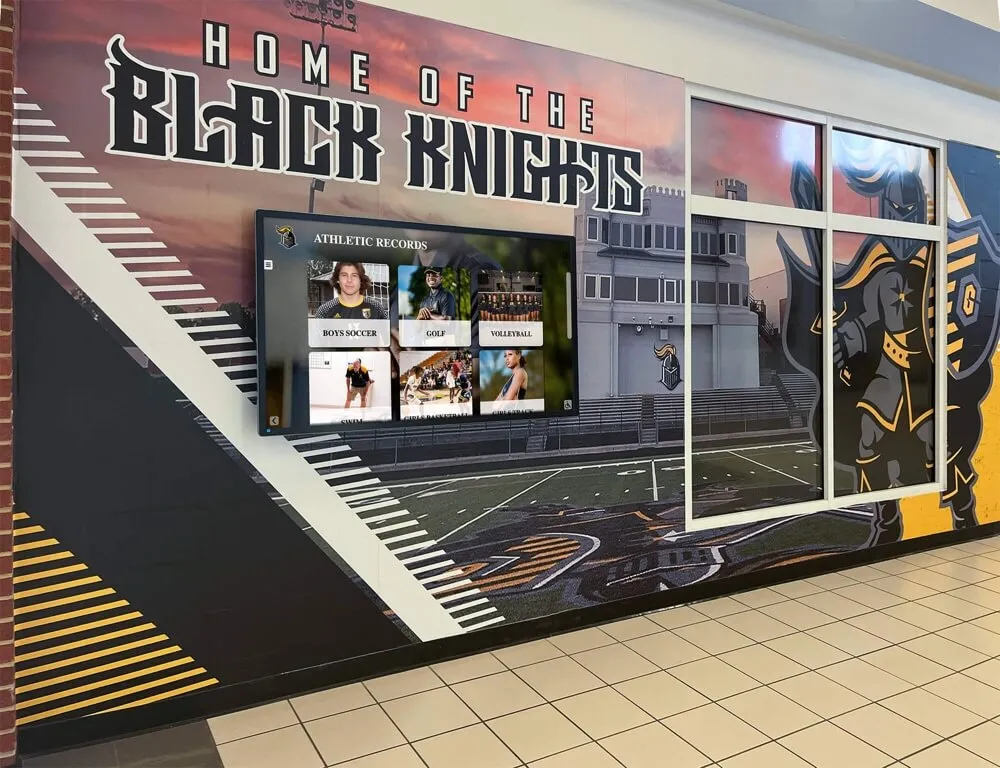
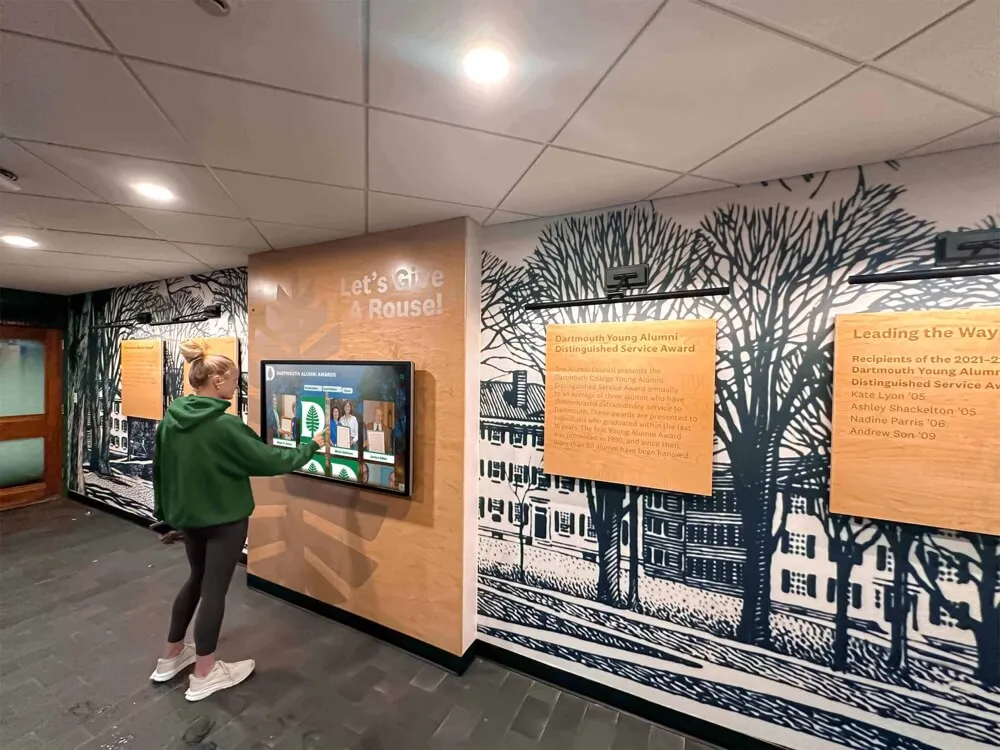
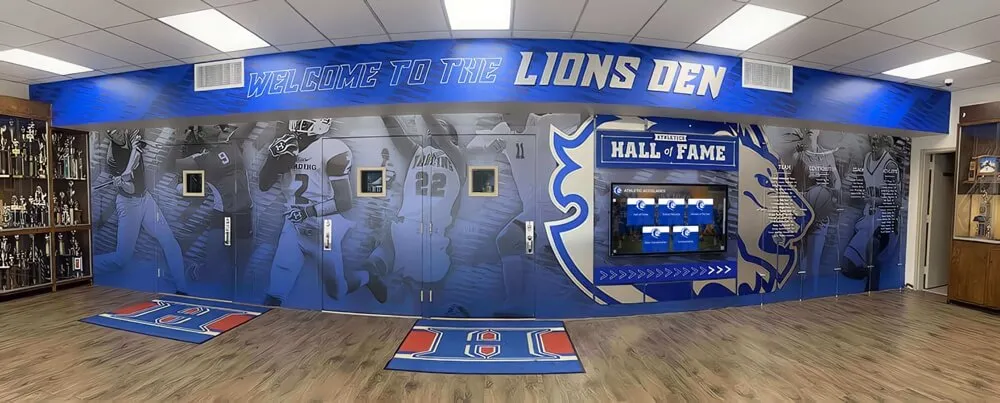
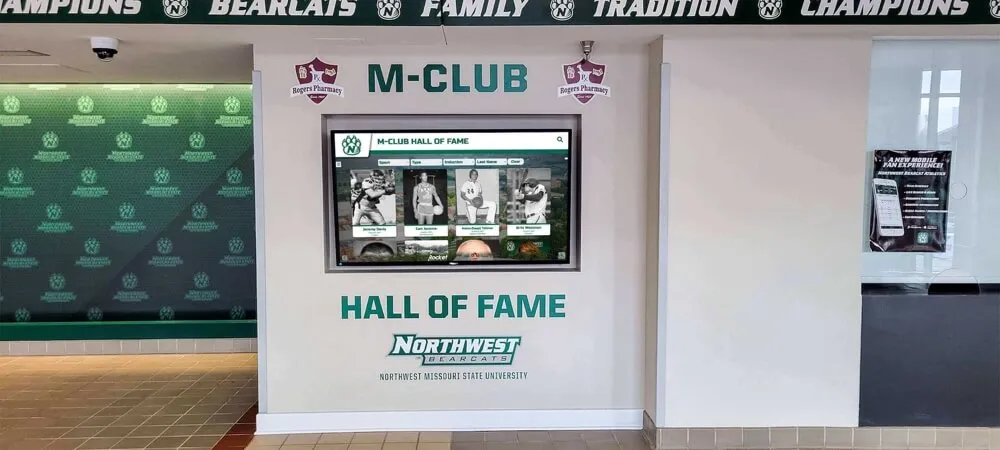
Interactive digital signage incorporating touchscreen capabilities transforms passive viewing experiences into engaging interactions where users explore content, search information, customize displays, or perform transactions—capabilities particularly valuable for wayfinding, directories, self-service kiosks, and educational recognition applications.
Touchscreen Technologies for Digital Signage
Capacitive Touch
Capacitive touchscreens, the technology used in smartphones and tablets, detect touch through electrical field disruptions created by conductive materials like human fingers. Multi-touch capacitive screens support gestures like pinch-to-zoom, swipe, and rotate that enable intuitive interaction with digital content.
Advantages of capacitive technology include highly responsive, accurate touch detection, support for multi-touch gestures, clear display without visible touch grid, and durability with glass surfaces resisting scratches and wear. Disadvantages include higher cost than alternative touch technologies and inability to detect touches through gloves or non-conductive styluses—potential limitations for outdoor applications in cold climates or industrial environments requiring protective equipment.
Infrared Touch
Infrared touchscreens create invisible infrared light grids across display surfaces, detecting touches when objects interrupt the beams. Large-format touchscreens—particularly 55-inch and larger interactive displays—commonly use infrared technology due to cost advantages at larger sizes and reliable performance across extended operational periods.
Infrared touch advantages include support for any input type (fingers, gloves, styluses), scalability to very large touch surfaces, no overlay obscuring display clarity, and reliable operation in various environmental conditions. Disadvantages include potential false triggers from debris or insects crossing the infrared beams and limited multi-touch capabilities in some implementations compared to capacitive alternatives.
Resistive Touch
Resistive touchscreens use pressure-sensitive overlays that complete electrical circuits when pressed, detecting touch location. While common in older touchscreen applications, resistive technology has largely been superseded by capacitive and infrared alternatives for digital signage due to inferior user experience and image clarity.
Resistive touch remains relevant primarily for budget-constrained applications, industrial environments requiring operation with heavy gloves, or outdoor installations where other technologies prove unreliable. Most modern interactive digital signage implementations avoid resistive touch in favor of superior alternatives providing better user experiences.
Interactive Digital Signage Applications
Wayfinding and Directories
Interactive displays excel in providing building directories, campus maps, and navigation assistance where users search for specific locations, departments, or individuals. Touchscreens enable intuitive map interaction with zoom, pan, and search capabilities impossible through passive displays requiring predetermined content sequences.
Successful wayfinding implementations feature clearly labeled interactive elements encouraging user engagement, search functionality finding destinations quickly, contextual information about points of interest, and “you are here” orientation helping users understand current position relative to destinations.
Information Kiosks and Self-Service
Self-service kiosks enable visitors to access information independently without staff assistance, serving applications like visitor check-in, event registration, product information, service directories, and form completion. Interactive digital signage reduces staffing requirements while providing convenient access to information outside normal business hours.
Organizations implementing self-service kiosks should design interfaces considering diverse user populations including those unfamiliar with touchscreen technology, ensure accessibility for users with disabilities, provide clear escape paths returning to main menus when users get lost, and implement automatic reset to attract mode after inactivity preventing subsequent users from seeing previous interactions.
Product Exploration and Configuration
Retail environments leverage interactive displays for product catalogs extending beyond physical inventory, customization tools allowing customers to configure products and visualize options, detailed product information including specifications and comparisons, and inventory checking showing product availability across locations.
Interactive product exploration creates engaging shopping experiences while providing functionality—like instantly accessing entire product catalogs or comparing features across multiple options—that physical displays cannot offer within constrained retail floor space.
Interactive Display Considerations
Durability and Maintenance
Public touchscreens endure constant physical interaction from diverse users, requiring robust construction withstanding continuous touch, impacts, scratches, and environmental exposure to oils, dirt, and moisture from user contact. Commercial-grade interactive displays implement protective glazing and sealed enclosures maintaining operation despite heavy public use.
Maintenance requirements include regular cleaning of touch surfaces, periodic calibration ensuring accurate touch detection, and monitoring for hardware wear requiring replacement before complete failure. Organizations should establish preventive maintenance schedules addressing these requirements proactively rather than reactive response to user complaints.

Interactive touchscreens create engaging experiences enabling users to explore content actively rather than passively viewing predetermined sequences
Software and Content Design
Interactive digital signage requires purpose-built software supporting touch interaction, user navigation, and content exploration rather than passive content management systems designed for broadcast digital signage. Organizations should evaluate interactive capabilities during software selection ensuring platforms adequately support planned interactive features.
Content design for interactive displays requires understanding user interface principles including clear visual affordances indicating touchable elements, consistent navigation patterns throughout the interface, appropriate text sizes and touch target dimensions for accurate interaction, and logical information architecture enabling intuitive exploration.
Screen Resolution Standards for Digital Signage
Display resolution dramatically impacts image clarity, text readability, and viewer experience—particularly important for digital signage applications where content consumption occurs from varying distances under diverse ambient conditions.
Common Resolution Standards
HD (1280×720) and Full HD (1920×1080)
High Definition provides adequate image quality for many digital signage applications, particularly displays viewed from moderate distances where increased resolution provides marginal improvements viewer’s don’t perceive. Full HD resolution, now the minimum specification for most commercial displays, ensures text readability and sharp images for typical viewing distances.
Content production for HD resolutions remains straightforward using standard design tools and asset libraries, avoiding the storage and bandwidth requirements higher resolutions impose. Many organizations find Full HD displays offer optimal balance of image quality, content production requirements, and equipment costs for general-purpose digital signage applications.
4K/Ultra HD (3840×2160)
4K resolution provides four times the pixel count of Full HD, enabling significantly closer viewing distances before pixelation becomes visible and substantially sharper text rendering particularly important for information-dense content or detailed imagery. Close-viewing applications—interactive kiosks, counter displays, indoor digital signage viewed within 6 feet—benefit substantially from 4K resolution improving text legibility and image quality noticeably compared to Full HD alternatives.
As 4K display prices have declined to near-parity with Full HD panels in many sizes, organizations increasingly specify 4K as standard rather than premium choice. The primary 4K considerations involve content production requirements and media player capabilities handling higher resolution content.
8K (7680×4320)
8K resolution remains premium specification offering marginal improvements over 4K for most digital signage applications. Viewing distances required to perceive difference between 4K and 8K resolution—typically under 3-4 feet for screens under 70 inches—fall outside typical signage viewing patterns except specialized applications.
Limited content availability, expensive media player requirements, and substantial price premiums over 4K alternatives restrict 8K adoption primarily to flagship installations showcasing cutting-edge technology regardless of practical necessity. Most organizations find 4K resolution provides entirely adequate image quality for digital signage applications without 8K’s additional costs and complexity.
Resolution and Viewing Distance Calculations
Optimal resolution selection depends on viewing distance and screen size relationships. Industry formulas suggest:
- Minimum viewing distance = Screen diagonal × 1.5 (for 4K) or × 2.5 (for Full HD)
- Maximum viewing distance for text readability = Screen diagonal × 4 (for typical font sizes)
A 55-inch 4K display provides sharp images from approximately 7 feet minimum, while Full HD requires approximately 11.5 feet before pixelation becomes imperceptible. Organizations should calculate these relationships for specific installation plans, selecting resolutions appropriate for actual viewing distances rather than simply choosing highest available specifications.
Specialized Screen Types for Unique Applications
Beyond mainstream display categories, specialized screen types serve niche digital signage applications where conventional displays prove inadequate or unconventional form factors enable unique implementations.
Ultra-Wide and Stretched Displays
Ultra-wide displays feature unconventional aspect ratios like 16:4, 32:9, or even 64:9 compared to standard 16:9 widescreen formats. These elongated screens serve applications including retail shelf-edge displays, transportation arrival/departure boards, menu boards presenting horizontal content arrangements, architectural elements where vertical space constraints limit standard format displays, and creative installations leveraging unusual proportions for visual impact.
Manufacturers offer bar-type LCD displays specifically designed for stretched applications, providing commercial-grade specifications in unusual form factors unattainable through consumer TV markets. Content production for non-standard aspect ratios requires custom design workflows rather than standard templates, increasing creative development complexity and costs.
Curved and Flexible Displays
Curved displays create immersive viewing experiences by wrapping content partially around viewers, particularly effective for video wall installations in control rooms, entertainment venues, and retail flagships. Concave curves enhance viewer immersion, while convex curves enable visibility from wider viewing angles in high-traffic locations.
OLED technology enables truly flexible displays bent to significant curves during installation, providing design flexibility impossible with rigid LCD panels. While curved displays command premium pricing and impose content production considerations ensuring graphics account for display curvature, unique visual impact justifies implementation in premium applications prioritizing differentiation and experience over cost optimization.
Mirror and Two-Way Mirror Displays
Mirror displays conceal screens behind semi-transparent mirrors, appearing as standard mirrors when displays power off while functioning as digital signage when activated. These specialty displays serve applications in retail fitting rooms, hospitality bathrooms, commercial building lobbies, and residential smart mirror installations where displays should integrate invisibly into environments when not actively used.
Two-way mirror implementation reduces effective display brightness by 40-60% due to light loss through the mirror layer, requiring very bright source panels—typically 500-800+ nits—to achieve acceptable image brightness in the final installation. Organizations should evaluate actual mirror display samples rather than standard displays when assessing content visibility for specific applications.
Outdoor High-Brightness Displays
Purpose-built outdoor displays implement specifications far exceeding standard commercial displays including 2,000-5,000+ nit brightness levels, IP65+ weatherproof enclosures, thermal management systems, anti-glare coatings reducing sunlight reflection, and commercial-grade panels designed for temperature extremes and continuous outdoor operation.
These specialized displays cost 2-5 times more than equivalent indoor displays due to ruggedized construction and extreme performance requirements. Organizations should resist attempting to deploy standard displays outdoors—insufficient brightness and weather protection will result in poor performance and premature failure regardless of protective enclosures applied after the fact.

Commercial displays integrate into diverse architectural environments with appropriate size, brightness, and form factor selection
Consumer TVs vs. Commercial Displays for Digital Signage
Organizations frequently consider repurposing consumer televisions for digital signage applications due to attractive pricing compared to commercial-grade displays. Understanding critical differences between consumer and commercial products helps inform appropriate technology selections.
Why Consumer TVs Appear Attractive
Consumer televisions offer compelling initial advantages including 30-50% lower purchase prices compared to similar-size commercial displays, widespread availability through consumer electronics retailers, familiar technology from residential applications, and extensive size ranges across competitive consumer markets.
These advantages create understandable appeal for budget-conscious organizations evaluating digital signage options. However, meaningful differences in specifications, durability, and operational capabilities make consumer televisions problematic for most commercial signage applications.
Critical Differences Between Consumer and Commercial Displays
Operational Ratings and Durability
Consumer televisions design specifications assume typical residential use—4-6 hours daily operation in climate-controlled environments with minimal mechanical stress. Commercial displays specifically engineer components and thermal management for 16-24 hour continuous operation across years without premature failure.
Deploying consumer TVs in commercial environments operating 12-16+ hours daily accelerates wear, often resulting in failures within 1-2 years compared to 5-7+ year expected lifespans of commercial equivalents. The 30-50% purchase price savings disappear quickly when premature replacements occur 2-3 times more frequently than commercial alternatives.
Brightness and Visibility
Consumer televisions typically provide 250-400 nits brightness optimized for controlled residential lighting conditions. Commercial environments—particularly spaces with significant natural light or bright overhead lighting—require 400-700+ nits brightness ensuring visibility despite ambient conditions consumer specifications never anticipated.
Organizations deploying consumer TVs in bright commercial environments frequently discover inadequate visibility requiring window treatments, lighting modifications, or display repositioning to achieve acceptable performance—additional expenses eliminating initial cost advantages while compromising installation flexibility.
Connectivity and Control Features
Commercial displays provide network control capabilities including remote power management, content scheduling, and system monitoring through Ethernet or RS-232 connections. These features enable centralized management of multi-display networks impossible with consumer televisions requiring physical interaction for power, input, and configuration management.
Consumer TVs implement “smart” features designed for residential entertainment—streaming apps, voice assistants, automatic content recognition—that provide no value for digital signage while creating potential security vulnerabilities and unexpected behavior in commercial deployments.
Warranty and Support
Consumer television warranties typically cover 1 year with residential use assumptions, while commercial display warranties commonly provide 3-5 years coverage specifically for commercial operation. Commercial warranty terms often include advance replacement, on-site service, and commercial support channels unavailable through consumer product support organizations.
The longer commercial warranties and professional support channels significantly reduce operational risk and total cost of ownership despite higher initial acquisition costs.
When Consumer TVs Might Be Acceptable
Limited scenarios exist where consumer televisions adequately serve digital signage needs including temporary displays operating under 6 months, low-usage applications operating under 4-6 hours daily, controlled indoor environments without brightness challenges, non-critical applications where failures create minimal business disruption, and extremely budget-constrained implementations accepting trade-offs between cost and performance.
Organizations considering consumer TVs should consciously acknowledge limitations and accept risks rather than expecting consumer products to perform equivalently to commercial alternatives across significantly different operational requirements.
Display Manufacturer and Brand Considerations
Digital signage display manufacturing concentrates among several major commercial display specialists and diversified electronics manufacturers offering professional display product lines.
Leading Commercial Display Manufacturers
Samsung
Samsung’s commercial display division offers comprehensive product lines spanning LCD and LED technologies, extensive size ranges from small format through video walls, competitive specifications and pricing, and strong distribution through commercial channels. Samsung displays serve digital signage applications globally across diverse industries and applications.
LG
LG Electronics provides commercial displays emphasizing OLED technology leadership alongside traditional LCD offerings, webOS signage platform integration, transparent OLED and specialty display options, and strong presence in premium commercial display markets prioritizing image quality and innovative form factors.
NEC Display Solutions
NEC specializes in commercial and professional displays with particular strength in video walls, large format displays, and mission-critical applications. NEC’s focus on commercial markets (versus diversified consumer electronics) provides deep expertise in digital signage requirements and professional support channels serving enterprise deployments.
Sony Professional Displays
Sony serves premium commercial display markets with emphasis on image quality, color accuracy, and high-end video wall applications. While typically commanding premium pricing, Sony displays appeal to applications prioritizing ultimate image quality and brand prestige over cost optimization.
Sharp/NEC Partnership
Following Sharp’s acquisition of NEC Display Solutions, the combined organization offers comprehensive commercial display products leveraging Sharp’s manufacturing scale and NEC’s commercial market expertise.
Evaluating Display Manufacturers
Product Range and Specifications
Assess whether manufacturers offer displays meeting your specific requirements including necessary sizes, brightness levels, resolution specifications, mounting options, and any specialty features like touchscreen capability or unusual aspect ratios.
Availability and Lead Times
Verify realistic product availability and delivery schedules rather than assuming advertised products ship immediately from stock. Supply chain disruptions affecting electronics industries generally create extended lead times for commercial displays, particularly larger sizes and specialty configurations.
Support and Warranty Coverage
Evaluate warranty terms, service response commitments, replacement part availability, and support channel quality. Premium manufacturers typically provide superior support infrastructure justifying modest price premiums through reduced operational risk and faster issue resolution.
Total Cost of Ownership
Compare comprehensive costs including initial acquisition price, expected lifespan and replacement frequency, warranty coverage and service costs, power consumption and operating expenses, and mounting/installation compatibility. The lowest purchase price rarely translates to lowest total cost across multi-year deployment periods.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
Operating costs and environmental impacts provide increasingly important selection criteria as organizations prioritize sustainability alongside performance and acquisition costs.
Power Consumption Across Display Technologies
LCD displays typically consume 50-150 watts for medium-format panels (43-55 inches) depending on brightness settings and backlight technology. LED-backlit panels generally achieve 20-30% better efficiency compared to older CCFL-backlit alternatives. OLED displays provide variable consumption depending on content—dark scenes consume minimal power while bright content may equal or exceed LCD consumption.
Direct-view LED displays consume substantially more power—typically 150-500+ watts for equivalent viewing areas depending on pixel pitch and brightness settings. Large outdoor LED displays draw multiple kilowatts during operation, creating significant ongoing electricity costs justifying LED primarily for applications requiring technology’s unique capabilities.
Energy-Saving Features
Modern commercial displays implement various energy management capabilities including automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light sensors, scheduled power management for automatic on/off based on occupancy schedules, low-power standby modes consuming under 1 watt when displays enter sleep states, and occupancy sensors detecting viewer presence to automatically wake displays from standby.
Organizations implementing large display networks should prioritize energy management features reducing consumption during unoccupied periods without requiring manual intervention. According to energy efficiency research, automated power management typically reduces overall consumption by 30-50% compared to displays operating continuously at fixed brightness levels.
Environmental Certifications
Several certification programs assess display environmental performance including ENERGY STAR ratings indicating efficient power consumption relative to typical products, EPEAT ratings evaluating comprehensive environmental attributes throughout product lifecycles, and RoHS compliance verifying restricted hazardous substance limitations in manufacturing.
Organizations with sustainability commitments should specify certified displays meeting relevant standards, communicating environmental priorities through procurement practices while reducing operational environmental impacts.
Choosing the Right Screen for Your Digital Signage Application
Systematic evaluation frameworks help organizations navigate complex technology choices, selecting displays optimally matching specific application requirements to available products.
Define Application Requirements
Environmental Conditions
Determine indoor versus outdoor placement, ambient lighting levels, temperature range exposure, humidity and moisture conditions, and physical security requirements influencing enclosure and mounting specifications.
Viewing Characteristics
Calculate typical viewing distances, viewing angle requirements, audience size and traffic patterns, and content types (text-heavy, image-focused, video-intensive) influencing resolution and size selection.
Operational Parameters
Specify daily operating hours, expected deployment duration, maintenance access capabilities, network connectivity availability, and budget constraints influencing technology and specification trade-offs.
Match Technologies to Requirements
Use application requirements to eliminate inappropriate technologies and narrow selection to suitable alternatives.
High ambient light or outdoor applications require LED or high-brightness LCD displays—eliminate standard LCD and OLED options offering insufficient brightness.
Close viewing distances favor high-resolution 4K displays—Full HD becomes acceptable only beyond 8-10 feet typical viewing.
Budget-constrained applications suggest standard commercial LCD displays—reserve premium OLED, MicroLED, or large LED video walls for applications justifying higher costs.
Interactive requirements necessitate touchscreen-equipped displays—specify capacitive technology for best user experience or infrared for large-format applications.
Evaluate Specific Products
Once technology categories align with requirements, evaluate specific manufacturer models including detailed specifications verification, warranty and support terms review, actual sample evaluation in environment similar to planned deployment, total cost of ownership calculation across expected lifespan, and reference checks with existing customers implementing similar applications.
Sample evaluation proves particularly important for subjective characteristics like image quality, color accuracy, viewing angle performance, and touchscreen responsiveness that specifications inadequately capture.
Implementation Planning
Successful display deployment requires planning beyond equipment selection including mounting and installation approach, content creation and management workflows, power and network infrastructure requirements, ongoing maintenance and support planning, and success measurement frameworks demonstrating business value.
Organizations should view display selection as initial step in comprehensive implementation projects rather than isolated equipment purchases disconnected from operational considerations determining long-term success.
Transform Your Communication with Professional Digital Signage
Whether you're implementing recognition displays, wayfinding systems, or promotional signage, selecting the right screen technology determines viewer experience, operational costs, and long-term success. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide proven digital display platforms specifically designed for institutional and organizational applications with appropriate hardware recommendations, content management capabilities, and ongoing support ensuring successful deployments.
Explore Digital Display SolutionsFuture Trends in Digital Signage Display Technology
Understanding emerging technologies and industry trends helps organizations make forward-looking investment decisions ensuring displays remain effective across multi-year deployment periods.
MicroLED Market Evolution
Industry analysts project MicroLED manufacturing costs declining substantially over the next 3-5 years as production scales, potentially enabling mainstream adoption in premium digital signage applications currently served by OLED or high-end LCD displays. Organizations planning significant display investments should monitor MicroLED market developments that may influence technology selection for deployments planned beyond 2026.
AI-Enhanced Display Management
Artificial intelligence integration enables displays to automatically adjust brightness based on ambient conditions and content, optimize power consumption based on occupancy patterns, detect and report technical issues before visible failures occur, and personalize content based on audience demographics detected through camera sensors.
These intelligent display capabilities reduce operational burden while improving performance, energy efficiency, and viewer experience—advantages likely to become standard features across commercial display products within coming years.
Higher Resolution Standards
While 8K resolution provides marginal benefits for most current digital signage applications, continued resolution advancement may enable new use cases including extremely close viewing without pixelation, high-detail imagery showcasing product textures and features, video wall seamlessness where bezels between panels become less noticeable at ultra-high resolutions, and creative applications leveraging resolution advantages for competitive differentiation.
Organizations should balance resolution specifications against actual requirements rather than simply pursuing maximum available specifications without corresponding benefits.
Sustainable Manufacturing and Circular Economy
Environmental considerations increasingly influence display technology development including reduced power consumption through more efficient components, longer operational lifespans extending useful product life, recyclable materials and modular designs facilitating component reuse, and take-back programs enabling responsible end-of-life disposal.
Organizations prioritizing sustainability should evaluate manufacturers’ environmental commitments and product attributes supporting circular economy principles rather than traditional linear consumption models.
Conclusion: Selecting Optimal Screens for Digital Signage Success
Choosing appropriate screen technology represents the foundation upon which effective digital signage programs build—optimal displays provide visibility, reliability, and performance enabling content to engage viewers and deliver measurable business value, while inadequate displays undermine even exceptional content through poor visibility, frequent failures, or inappropriate specifications limiting effectiveness.
The comprehensive screen technology landscape—spanning LCD in various panel types, direct-view LED across numerous pixel pitches, OLED with exceptional image quality, emerging MicroLED combining technologies’ best attributes, and specialized displays serving unique applications—ensures suitable options exist for virtually any digital signage requirement. Success requires matching specific technologies to actual application needs rather than selecting based on general recommendations disconnected from particular environmental conditions, viewing characteristics, operational parameters, and budget constraints shaping individual projects.
Organizations implementing digital signage should systematically evaluate requirements before exploring specific products, eliminating inappropriate technologies early in selection processes while focusing detailed evaluation on alternatives genuinely suitable for planned applications. This disciplined approach prevents pursuing attractive specifications or pricing for technologies fundamentally mismatched to environmental conditions, viewing distances, or operational demands determining real-world performance.

Successful digital signage combines appropriate screen technology with thoughtful content, strategic placement, and reliable operation creating lasting value
Beyond initial technology selection, total cost of ownership analysis proves essential for informed decisions—comparing not just purchase prices but comprehensive costs including installation, power consumption, maintenance, expected lifespan, and replacement frequency across alternatives. Premium displays commanding higher acquisition costs frequently deliver lower total ownership costs through extended lifespans, superior reliability, better energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance requirements that offset initial price premiums.
The distinction between consumer and commercial-grade displays proves particularly important for organizations tempted by consumer television pricing without recognizing critical specification and durability differences. Commercial displays design specifically for continuous operation in demanding commercial environments, providing brightness levels, connectivity features, warranty coverage, and expected lifespans that consumer products cannot match regardless of initial cost advantages.
As display technology continues evolving—with MicroLED approaching commercial viability, AI integration enabling intelligent operation, higher resolutions expanding creative possibilities, and sustainability considerations influencing manufacturing approaches—organizations should select flexible platforms supporting emerging capabilities through updates and enhancements rather than requiring complete replacement when new features become available.
Start by clearly defining your specific digital signage requirements including environmental conditions, viewing characteristics, operational parameters, and budget constraints. Use these requirements to systematically eliminate inappropriate technologies while focusing evaluation on genuinely suitable alternatives. Evaluate actual product samples in conditions approximating real deployment environments rather than relying solely on specifications. Calculate comprehensive total cost of ownership across expected lifespans. And partner with experienced manufacturers and integrators providing not just quality products but expertise and support ensuring successful long-term operation.
Digital signage success begins with appropriate screen technology—but extends far beyond equipment specifications to encompass content quality, strategic placement, reliable operations, and continuous optimization delivering sustained business value. The comprehensive understanding of screen technologies, specifications, applications, and selection criteria explored throughout this guide provides the foundation for confident decisions launching effective digital signage programs serving organizational goals across years of reliable operation.
Ready to implement digital signage displays optimally matched to your specific requirements? Explore how solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions combine appropriate display technology with purpose-built content management platforms serving diverse applications from educational recognition systems to corporate communication displays, providing proven platforms delivering lasting value through thoughtful technology selection, comprehensive implementation support, and ongoing innovation addressing evolving organizational needs.